Parsing XML with Python: A Comprehensive Guide
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a widely used format for storing and transporting data. Its human-readable structure and platform independence make it a popular choice for configuration files, data exchange between systems, and more. Python, with its rich ecosystem of libraries, offers several tools for parsing XML documents efficiently and effectively. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to parse XML data using Python, covering different libraries and techniques, ensuring you can handle various XML structures with ease.
Why Parse XML with Python?
Python’s versatility and ease of use make it an ideal language for working with XML data. Several libraries in Python simplify the process of parsing XML, allowing developers to focus on extracting and manipulating the data rather than dealing with the complexities of the XML format itself. Whether you’re extracting data from a configuration file, processing data from a web service, or transforming XML documents, Python provides the tools you need.
Popular Python Libraries for Parsing XML
Several Python libraries are available for parsing XML, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The most commonly used libraries include:
- xml.etree.ElementTree (ElementTree): Part of Python’s standard library, ElementTree provides a simple and lightweight way to parse XML documents. It’s efficient and easy to use, making it a good choice for most common XML parsing tasks.
- xml.dom.minidom (minidom): Another part of the standard library, minidom implements the Document Object Model (DOM) API. It loads the entire XML document into memory, creating a tree-like structure that can be traversed and manipulated.
- lxml: A third-party library that provides a high-performance XML parsing solution. It supports both ElementTree and XPath, offering a more powerful and flexible way to parse XML documents. Lxml is generally faster and more feature-rich than the standard library options.
Using ElementTree for Parsing XML
ElementTree is a popular choice for parsing XML due to its simplicity and efficiency. Here’s how to use it:
Importing the Library
First, import the ElementTree library:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ETParsing an XML File
To parse XML from a file, use the ET.parse() function:
tree = ET.parse('example.xml')
root = tree.getroot()Here, example.xml is the name of the XML file you want to parse. The getroot() method returns the root element of the XML document.
Parsing an XML String
If you have an XML string, you can use the ET.fromstring() function:
xml_string = '<root><element>Data</element></root>'
root = ET.fromstring(xml_string)Accessing Elements
You can access elements using various methods:
- Tag: The name of the element.
- Attributes: A dictionary of attributes associated with the element.
- Text: The text content of the element.
for element in root:
print(f'Tag: {element.tag}')
print(f'Attributes: {element.attrib}')
print(f'Text: {element.text}')Finding Elements
ElementTree provides methods for finding specific elements within the XML document:
- find(match): Finds the first element matching the specified tag.
- findall(match): Finds all elements matching the specified tag.
- iter(tag=None): Creates an iterator for all subelements, optionally filtered by tag.
for element in root.findall('element'):
print(element.text)Using minidom for Parsing XML
The xml.dom.minidom library provides a DOM-based approach to parsing XML. This means it loads the entire XML document into memory as a tree structure. While it can be memory-intensive for large documents, it offers a convenient way to navigate and manipulate the XML structure.
Importing the Library
Import the minidom library:
from xml.dom import minidomParsing an XML File
To parse XML from a file, use the minidom.parse() function:
dom = minidom.parse('example.xml')Parsing an XML String
If you have an XML string, you can use the minidom.parseString() function:
xml_string = '<root><element>Data</element></root>'
dom = minidom.parseString(xml_string)Accessing Elements
You can access elements using various methods:
- getElementsByTagName(tagname): Returns a list of elements with the specified tag name.
- attributes: A NamedNodeMap of attributes associated with the element.
- firstChild: The first child node of the element.
- childNodes: A list of child nodes of the element.
elements = dom.getElementsByTagName('element')
for element in elements:
print(element.firstChild.data)Using lxml for Parsing XML
lxml is a powerful and efficient third-party library for parsing XML and HTML. It offers better performance than the standard library options and supports XPath, a query language for selecting nodes from an XML document.
Installing lxml
First, install the lxml library using pip:
pip install lxmlImporting the Library
Import the lxml.etree module:
from lxml import etreeParsing an XML File
To parse XML from a file, use the etree.parse() function:
tree = etree.parse('example.xml')
root = tree.getroot()Parsing an XML String
If you have an XML string, you can use the etree.fromstring() function:
xml_string = '<root><element>Data</element></root>'
root = etree.fromstring(xml_string)Accessing Elements
You can access elements using similar methods to ElementTree:
for element in root:
print(f'Tag: {element.tag}')
print(f'Attributes: {element.attrib}')
print(f'Text: {element.text}')Using XPath
XPath allows you to select nodes from an XML document using a path-like syntax. This is a powerful way to query and extract data from complex XML structures.
elements = root.xpath('//element')
for element in elements:
print(element.text)The expression '//element' selects all <element> tags in the document.
Handling Namespaces
XML namespaces are used to avoid naming conflicts when combining XML documents from different sources. When parsing XML documents with namespaces, you need to be aware of the namespace URIs and use them when accessing elements.
Registering Namespaces
With ElementTree and lxml, you can register namespaces using a dictionary:
namespaces = {'prefix': 'http://example.com/namespace'}
root.find('prefix:element', namespaces)Error Handling
When parsing XML, it’s important to handle potential errors, such as malformed XML or missing elements. You can use try-except blocks to catch exceptions and handle them gracefully.
try:
tree = ET.parse('invalid.xml')
except ET.ParseError as e:
print(f'Error parsing XML: {e}')Real-World Examples
Let’s look at some real-world examples of parsing XML with Python.
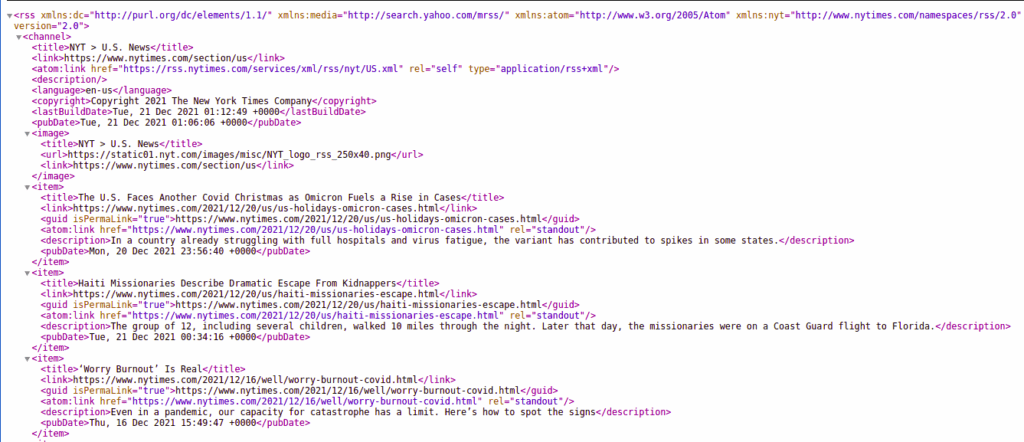
Parsing RSS Feeds
RSS (Really Simple Syndication) feeds are commonly used to distribute news and blog content. You can use Python to parse RSS feeds and extract the titles, descriptions, and links of the articles.
import requests
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
url = 'https://www.example.com/rss'
response = requests.get(url)
xml_string = response.text
tree = ET.fromstring(xml_string)
for item in tree.findall('.//item'):
title = item.find('title').text
link = item.find('link').text
print(f'Title: {title}')
print(f'Link: {link}')Parsing Configuration Files
XML is often used for configuration files. You can use Python to parse these files and extract the configuration settings.
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse('config.xml')
root = tree.getroot()
settings = {}
for setting in root.findall('setting'):
name = setting.get('name')
value = setting.text
settings[name] = value
print(settings)Best Practices for Parsing XML with Python
- Choose the right library: Consider the size and complexity of your XML documents when choosing a parsing library. ElementTree is suitable for most common tasks, while lxml offers better performance and XPath support for more complex scenarios.
- Handle errors: Implement proper error handling to gracefully handle malformed XML or missing elements.
- Use namespaces: Be aware of namespaces when parsing XML documents with namespaces and use them when accessing elements.
- Optimize performance: For large XML documents, consider using iterative parsing techniques or libraries like lxml to improve performance.
- Validate XML: Before parsing, validate the XML document against a schema to ensure it is well-formed and conforms to the expected structure.
Conclusion
Parsing XML with Python is a straightforward process thanks to the availability of powerful libraries like ElementTree, minidom, and lxml. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each library and following best practices, you can efficiently extract and manipulate XML data for various applications. Whether you’re processing RSS feeds, configuration files, or data from web services, Python provides the tools you need to handle XML parsing effectively. [See also: Python XML Processing Libraries] Understanding how to parse XML is crucial for any developer working with data interchange and configuration management. With the right techniques and libraries, parsing XML in Python can be a breeze.
