A Proxy Is: Understanding Its Function, Benefits, and Security Implications
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, understanding the tools and technologies that facilitate secure and efficient online communication is paramount. One such tool is a proxy. But what exactly is a proxy? At its core, a proxy acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. Think of it as a middleman handling requests and responses, offering a layer of separation and control. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of a proxy, exploring its various types, benefits, use cases, and potential security considerations. We will examine how a proxy server works, why individuals and organizations utilize them, and the implications for privacy and security. Understanding what a proxy is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern internet.
What Exactly Is A Proxy Server?
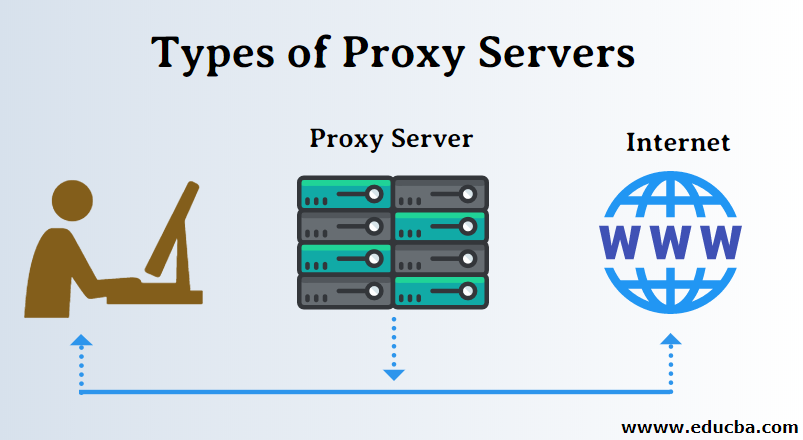
A proxy server, often simply called a proxy, is a computer system or application that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. Instead of connecting directly to the origin server, the client connects to the proxy server, which then evaluates the request and either fulfills it itself or forwards it to the origin server. The origin server then sends the response back to the proxy, which in turn forwards it to the client. This process masks the client’s IP address, providing a degree of anonymity.
To illustrate, imagine you’re trying to access a website. Without a proxy, your computer directly connects to the website’s server. With a proxy, your computer connects to the proxy server, which then connects to the website on your behalf. The website sees the proxy server’s IP address, not yours. This simple act has profound implications for privacy, security, and access control.
Types of Proxy Servers
Proxy servers come in various forms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these different types is essential for choosing the right proxy for your needs.
Forward Proxies
A forward proxy, also known as a client-side proxy, is the most common type. It sits in front of a client or a group of clients, forwarding requests to the internet. This type of proxy is often used by organizations to control internet access for their employees, improve security, and cache frequently accessed content to reduce bandwidth usage. [See also: Corporate Network Security Best Practices]
Reverse Proxies
A reverse proxy, on the other hand, sits in front of one or more web servers, directing client requests to those servers. It’s often used to improve performance, security, and reliability of web applications. Reverse proxies can handle tasks such as load balancing, SSL encryption, and caching static content, freeing up the web servers to focus on dynamic content generation. [See also: Web Server Optimization Techniques]
Transparent Proxies
A transparent proxy intercepts client requests without the client’s knowledge or configuration. These proxies are often used by ISPs or network administrators to enforce policies, cache content, or filter traffic. While convenient for the administrator, transparent proxies can raise privacy concerns if users are unaware that their traffic is being monitored or modified.
Anonymous Proxies
Anonymous proxies are designed to hide the client’s IP address, providing a degree of anonymity. However, some anonymous proxies still reveal that a proxy is being used. These are sometimes called distorting proxies, as they present a fake IP address but still identify themselves as proxies.
Elite Proxies
Elite proxies, also known as high-anonymity proxies, provide the highest level of anonymity by not only hiding the client’s IP address but also not revealing that a proxy is being used. This makes it difficult to trace the client’s activity back to their original IP address.
SOCKS Proxies
SOCKS (Socket Secure) is an internet protocol that routes network packets between a client and server through a proxy server. Unlike HTTP proxies, SOCKS proxies can handle any type of traffic, including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and SMTP. This makes them more versatile but also potentially more complex to configure. [See also: Understanding Network Protocols]
Benefits of Using a Proxy
The use of a proxy server offers several compelling advantages for both individuals and organizations.
Enhanced Security
Proxy servers can act as a buffer between your device and the internet, protecting you from malicious attacks and unwanted traffic. They can filter out harmful content, block access to known malicious websites, and prevent direct connections between your device and potential threats. Furthermore, a reverse proxy can protect web servers from DDoS attacks by absorbing the initial flood of traffic. [See also: Cybersecurity Threats and Prevention]
Improved Privacy
By masking your IP address, a proxy can help protect your online privacy. Websites and online services will see the proxy server’s IP address instead of your own, making it more difficult to track your online activity. This is particularly useful when accessing websites or services that you don’t fully trust. However, it’s important to choose a reputable proxy provider, as some may log your traffic and compromise your privacy. [See also: Online Privacy and Data Protection]
Access Control
Organizations can use proxies to control internet access for their employees. They can block access to specific websites or categories of websites, enforce acceptable use policies, and monitor employee internet usage. This helps to improve productivity, prevent the spread of malware, and reduce the risk of legal liability. [See also: Employee Internet Usage Policies]
Bypass Geo-Restrictions
Some websites and online services restrict access based on geographic location. By using a proxy server located in a different country, you can bypass these restrictions and access content that would otherwise be unavailable. This is particularly useful for accessing streaming services or news websites that are blocked in your region. However, it’s important to be aware of the terms of service of the websites or services you’re accessing, as bypassing geo-restrictions may violate their policies.
Improved Performance
Proxy servers can cache frequently accessed content, reducing the load on origin servers and improving response times for clients. When a client requests content that is already cached on the proxy server, the proxy can serve the content directly, without having to forward the request to the origin server. This can significantly improve performance, especially for websites with a large number of users. [See also: Website Performance Optimization]
Potential Security Considerations
While proxy servers offer numerous benefits, it’s important to be aware of the potential security risks associated with their use.
Proxy Logging
Many proxy servers log user activity, including IP addresses, websites visited, and timestamps. This data can be used to track your online activity and potentially compromise your privacy. It’s important to choose a proxy provider that has a clear and transparent privacy policy and that does not log your traffic unnecessarily. [See also: Data Logging and Privacy Regulations]
Malicious Proxies
Some proxy servers are operated by malicious actors who may use them to steal your data, inject malware into your traffic, or redirect you to phishing websites. It’s important to be cautious when choosing a proxy provider and to avoid using free or untrusted proxies. Look for reputable providers with a proven track record of security and reliability. [See also: Identifying and Avoiding Phishing Scams]
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Proxy servers can be vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks, where an attacker intercepts traffic between your device and the proxy server. This allows the attacker to eavesdrop on your communication, steal your data, or modify your traffic. To mitigate this risk, it’s important to use HTTPS connections whenever possible and to choose a proxy provider that uses strong encryption. [See also: Understanding Encryption Technologies]
Conclusion
A proxy server is a valuable tool for enhancing security, improving privacy, and controlling internet access. By acting as an intermediary between your device and the internet, a proxy can provide a layer of protection and control. However, it’s important to understand the different types of proxies, their benefits, and their potential security risks. By choosing a reputable proxy provider and following best practices for online security, you can leverage the power of a proxy to enhance your online experience. Understanding what a proxy is and how it functions is increasingly essential in today’s digital world, empowering users to make informed decisions about their online security and privacy. Whether you are an individual seeking greater anonymity or an organization striving to manage network access, a proxy can be a powerful ally. Choosing the right proxy and understanding its implications is key to reaping its benefits safely and effectively. Always prioritize security and privacy when selecting and using a proxy service. Remember that a proxy is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to overall online security and privacy; a comprehensive approach is always recommended.
