Proxying Definition: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Proxies
In the digital age, understanding the nuances of internet security and network architecture is crucial. One fundamental concept is proxying. This article provides a comprehensive proxying definition, exploring its functionalities, benefits, and various applications. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or simply curious about enhancing your online security, understanding what proxying entails is essential.
What is Proxying? A Detailed Proxying Definition
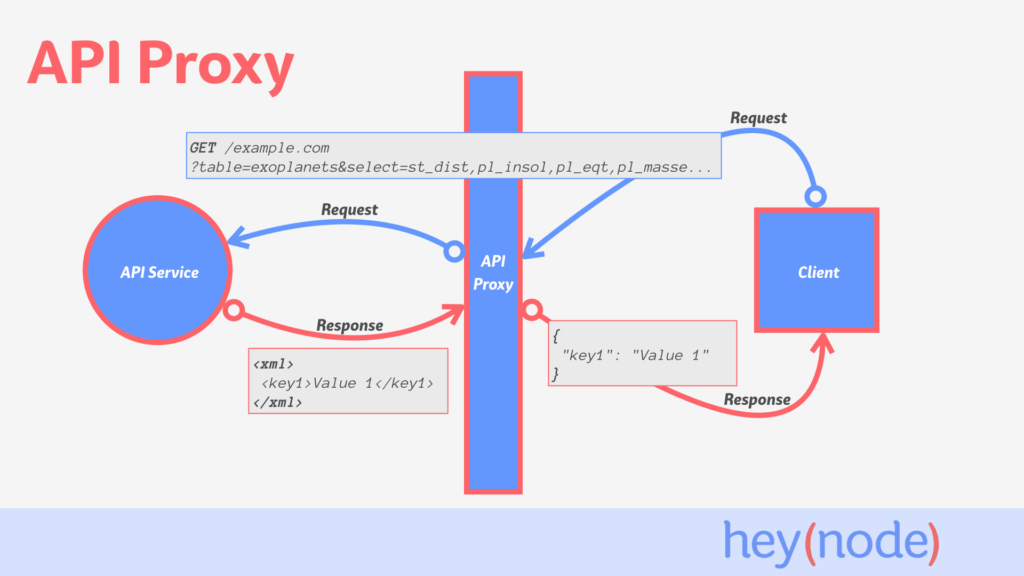
At its core, proxying involves using a server, known as a proxy server, to act as an intermediary between your device and the internet. Instead of directly connecting to a website or online service, your request is routed through the proxy server. This server then forwards the request on your behalf, receives the response, and relays it back to you. This process masks your IP address, providing a layer of anonymity and security.
A proxying setup can be visualized as a gateway. When you want to access a website, your request doesn’t go directly to that website. Instead, it goes to the proxy server. The proxy server then fetches the website on your behalf and sends it back to you. The website only sees the IP address of the proxy server, not your actual IP address.
The Mechanics of Proxy Servers
To fully grasp the proxying definition, it’s important to understand how proxy servers function. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
- Request Initiation: You initiate a request to access a website or online resource.
- Request Routing: Your request is routed to the proxy server.
- IP Masking: The proxy server masks your IP address and replaces it with its own.
- Request Forwarding: The proxy server forwards the request to the target website or service.
- Response Retrieval: The target website sends the response back to the proxy server.
- Response Delivery: The proxy server relays the response back to your device.
This process ensures that your actual IP address remains hidden from the target website, enhancing your privacy and security. Understanding this flow is crucial for anyone looking to implement proxying effectively.
Types of Proxy Servers
The proxying definition encompasses various types of proxy servers, each with its own specific functionalities and applications:
HTTP Proxies
HTTP proxies are designed for handling web traffic. They are commonly used to cache web pages, filter content, and bypass geographical restrictions. When you access a website through an HTTP proxy, the proxy server fetches the web page and stores a copy. If another user requests the same web page, the proxy server can serve the cached version, reducing bandwidth usage and improving loading times.
HTTPS Proxies
HTTPS proxies provide an additional layer of security by encrypting the data transmitted between your device and the proxy server. This is particularly useful when accessing sensitive information online, such as banking details or personal data. HTTPS proxies ensure that your data remains secure and protected from eavesdropping.
SOCKS Proxies
SOCKS proxies are more versatile than HTTP and HTTPS proxies, as they can handle any type of network traffic. They are often used for applications that require a high degree of anonymity, such as torrenting or accessing restricted content. SOCKS proxies operate at a lower level of the network protocol stack, making them more flexible and adaptable.
Transparent Proxies
Transparent proxies are designed to intercept and redirect network traffic without the user’s knowledge. They are commonly used in corporate networks and public Wi-Fi hotspots to monitor and filter internet usage. Transparent proxies can also be used to cache web pages and optimize network performance.
Reverse Proxies
Reverse proxies are deployed on the server-side to protect web servers from direct exposure to the internet. They act as an intermediary between the internet and the web server, filtering malicious traffic and distributing the load across multiple servers. Reverse proxies can also be used to cache content and improve website performance.
Benefits of Using Proxy Servers
Understanding the proxying definition also means acknowledging the numerous benefits that proxy servers offer:
- Enhanced Security: Proxy servers mask your IP address, making it more difficult for hackers to track your online activity.
- Improved Privacy: By hiding your IP address, proxy servers protect your personal information from being exposed to websites and online services.
- Bypassing Geographical Restrictions: Proxy servers allow you to access content that is restricted in your region by routing your traffic through a server in a different location.
- Content Filtering: Proxy servers can be configured to block access to certain websites or types of content, making them useful for parental control and corporate network management.
- Improved Performance: Proxy servers can cache frequently accessed content, reducing bandwidth usage and improving website loading times.
Use Cases for Proxying
The applications of proxying are vast and varied. Here are some common use cases:
Web Scraping
Web scraping involves extracting data from websites. Proxy servers are used to rotate IP addresses, preventing your scraping activities from being blocked by websites. By using multiple proxy servers, you can distribute your requests and avoid being detected as a bot.
Social Media Management
Social media managers often use proxy servers to manage multiple accounts from a single device. Proxy servers allow you to assign a different IP address to each account, preventing them from being linked or flagged by social media platforms.
Market Research
Market researchers use proxy servers to gather data from different geographical locations. By routing your traffic through proxy servers in various countries, you can access region-specific data and gain insights into different markets.
Online Gaming
Online gamers use proxy servers to reduce latency and improve their gaming experience. By connecting to a proxy server that is located closer to the game server, you can minimize lag and improve responsiveness. Additionally, proxies help bypass geo-restrictions and access games not available in your region.
SEO Monitoring
SEO professionals use proxy servers to monitor search engine rankings from different locations. By routing your traffic through proxy servers in various cities, you can see how your website ranks in different search results and optimize your SEO strategy accordingly.
Potential Drawbacks of Using Proxy Servers
While proxying offers numerous benefits, it’s important to be aware of the potential drawbacks:
- Slower Connection Speeds: Routing your traffic through a proxy server can sometimes result in slower connection speeds, especially if the proxy server is located far away or is overloaded.
- Security Risks: Not all proxy servers are created equal. Some proxy servers may be operated by malicious actors who can intercept your data and steal your personal information. It’s important to choose a reputable proxy server provider and ensure that the proxy server uses encryption.
- Logging of Activity: Some proxy servers may log your online activity, which can compromise your privacy. It’s important to read the proxy server’s privacy policy and understand how your data is being used.
- Compatibility Issues: Some websites and applications may not be compatible with proxy servers. This can result in errors or prevent you from accessing certain content.
Choosing the Right Proxy Server
Selecting the right proxy server is crucial for ensuring your online security and privacy. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a proxy server:
- Reputation: Choose a proxy server provider with a good reputation and a proven track record of providing reliable and secure service.
- Location: Select a proxy server that is located in a geographical region that meets your needs. If you want to access content that is restricted in your region, choose a proxy server in a different location.
- Speed: Test the speed of the proxy server to ensure that it provides a fast and reliable connection.
- Security: Ensure that the proxy server uses encryption to protect your data from being intercepted.
- Logging Policy: Read the proxy server’s privacy policy to understand how your data is being used and whether your online activity is being logged.
- Cost: Proxy servers can range in price from free to hundreds of dollars per month. Consider your budget and choose a proxy server that offers the features and performance you need at a price you can afford.
The Future of Proxying
As the internet continues to evolve, proxying will remain an important tool for enhancing online security and privacy. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats and data breaches, more and more individuals and organizations are turning to proxy servers to protect their sensitive information. Furthermore, the rise of remote work and global business has increased the need for bypassing geographical restrictions and accessing content from different locations.
Technological advancements are also shaping the future of proxying. The development of more sophisticated proxy server technologies, such as rotating proxies and residential proxies, is making it more difficult for websites to detect and block proxy traffic. Additionally, the integration of proxy servers with other security tools, such as VPNs and firewalls, is providing a more comprehensive approach to online security.
Conclusion: Embracing the Proxying Definition
Understanding the proxying definition is paramount in today’s digital landscape. Whether you’re looking to enhance your online security, bypass geographical restrictions, or improve your browsing experience, proxy servers offer a versatile and effective solution. By carefully considering the different types of proxy servers and their associated benefits and drawbacks, you can make an informed decision and choose the right proxy server for your needs. As technology continues to advance, proxying will undoubtedly remain a critical component of online security and privacy.
By understanding the nuances of proxying, users can navigate the internet with greater confidence and security. This comprehensive guide has provided a thorough proxying definition, equipping readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their online activities. [See also: VPN vs Proxy: What’s the Difference?] [See also: How to Set Up a Proxy Server] [See also: Best Proxy Server Providers].
