Understanding and Managing Your IP Address Change
In today’s interconnected world, understanding your IP address and how it can change is crucial for both personal and professional reasons. An IP address, or Internet Protocol address, is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. Think of it as your device’s digital mailing address. This article delves into the intricacies of IP address changes, exploring why they occur, the different types of IP addresses, and how you can manage or even initiate an IP change address process.
What is an IP Address?
An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing. It enables devices to communicate with each other over the internet. Without an IP address, sending and receiving data across the internet would be impossible. Every device, from your smartphone to your smart refrigerator, requires an IP address to participate in the digital ecosystem.
Types of IP Addresses
There are primarily two versions of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numerical addresses, typically represented in dotted decimal notation (e.g., 192.168.1.1). IPv6 addresses, on the other hand, are 128-bit alphanumeric addresses designed to overcome the limitations of IPv4. With the exponential growth of internet-connected devices, IPv6 provides a significantly larger address space, ensuring each device can have a unique identifier. [See also: What is IPv6 and Why Does It Matter?]
Beyond the version, IP addresses can also be categorized as public or private. A public IP address is assigned to your network by your internet service provider (ISP) and is visible to the entire internet. It’s the address that other devices use to communicate with your network. A private IP address, conversely, is used within your private network (e.g., your home or office network). These addresses are not directly accessible from the internet and are typically assigned by your router.
Why Does Your IP Address Change?
An IP address change is a common occurrence. Several factors can trigger this, and understanding them can help you manage your network more effectively. The most common reasons include:
- Dynamic IP Allocation: Most ISPs use dynamic IP addressing, which means they assign IP addresses to users from a pool of available addresses. These addresses are not permanently assigned to one user but are leased for a specific period. When the lease expires, the ISP may assign a new IP address, leading to an IP change address.
- Router Restart: Restarting your router often triggers a request for a new IP address from your ISP. This is because the router essentially forgets its previous assignment and initiates a new connection.
- Network Configuration Changes: Changes to your network configuration, such as adding or removing devices or modifying router settings, can also prompt an IP address change.
- ISP Maintenance: ISPs periodically perform maintenance on their networks, which may involve reassigning IP addresses to optimize network performance or address technical issues.
- Moving Locations: If you physically move your internet connection to a new location, your ISP will assign you a new IP address that corresponds to your new geographical area.
Understanding Dynamic vs. Static IP Addresses
As mentioned earlier, most ISPs use dynamic IP addressing. This is a cost-effective and efficient way to manage IP address resources. However, some users may opt for a static IP address. A static IP address is a permanently assigned address that does not change unless manually reconfigured. Businesses often prefer static IP addresses for hosting servers, running websites, or enabling remote access to their networks. While static IP addresses offer stability and predictability, they typically come at an additional cost and require more technical expertise to manage. If you want to avoid an IP change address, a static IP is the way to go.
How to Check Your IP Address
Checking your IP address is a straightforward process. There are several online tools and methods you can use:
- Online IP Address Lookup Tools: Numerous websites, such as WhatIsMyIP.com or IPLocation.net, can instantly display your public IP address. Simply visit one of these sites, and it will automatically detect and display your IP address.
- Router Configuration: You can also find your IP address in your router’s configuration settings. The exact steps vary depending on your router model, but generally, you can access the router’s web interface by typing its default gateway address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into your web browser. Look for a section labeled “Status,” “WAN,” or “Internet” to find your IP address.
- Command Line (Windows): Open the Command Prompt and type
ipconfig. Look for the “IPv4 Address” under your network adapter. - Terminal (macOS/Linux): Open the Terminal and type
ifconfig. Look for the “inet” address under your network interface.
How to Change Your IP Address
While you typically cannot directly choose your IP address, you can initiate an IP change address in several ways:
- Restart Your Router: As mentioned earlier, restarting your router is the easiest and most common way to request a new IP address from your ISP. Simply unplug your router, wait for about 30 seconds, and then plug it back in. Once the router reconnects to the internet, it will likely be assigned a new IP address.
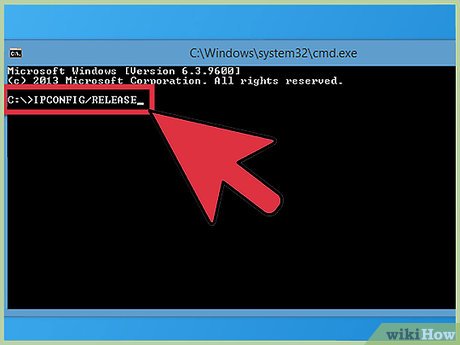
- Release and Renew Your IP Address: You can manually release your current IP address and request a new one through your operating system’s network settings. On Windows, open the Command Prompt as an administrator and type
ipconfig /releasefollowed byipconfig /renew. On macOS, go to System Preferences > Network, select your network interface, click “Advanced,” and then click the “TCP/IP” tab. Click the “Renew DHCP Lease” button. - Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network): A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a server in a different location. This effectively masks your real IP address and replaces it with the IP address of the VPN server. This method is useful for enhancing privacy and security, as well as accessing content that may be restricted in your region. [See also: Best VPN Services for Privacy and Security]
- Contact Your ISP: In some cases, you may need to contact your ISP directly to request a new IP address. This is more common if you have a static IP address or if you are experiencing persistent network issues.
Implications of an IP Address Change
An IP address change can have various implications, depending on your online activities and network configuration. For most users, the change is seamless and does not cause any noticeable disruptions. However, in certain situations, it can affect:
- Remote Access: If you rely on remote access to your home or office network, a change in your public IP address may require you to update your remote access settings.
- Online Gaming: Some online games may temporarily disconnect you if your IP address changes during gameplay.
- Security Settings: If you have configured security settings that rely on your IP address (e.g., whitelisting your IP address for access to certain services), you may need to update these settings after an IP change address.
- Website Hosting: If you are hosting a website or server on your home network, a static IP address is essential to ensure consistent accessibility.
IP Address Security and Privacy
Your IP address can be used to infer your approximate location and track your online activities. While it does not reveal your exact identity, it can be combined with other data to create a profile of your online behavior. To protect your privacy, consider using a VPN or a proxy server to mask your IP address and encrypt your internet traffic. Regularly checking your IP address and understanding how it changes can also help you monitor your online security and privacy.
Conclusion
Understanding the dynamics of IP address changes is essential for navigating the modern digital landscape. Whether you’re a casual internet user or a seasoned network administrator, knowing why IP change addresses occur and how to manage them can empower you to maintain a secure and efficient online experience. By understanding the different types of IP addresses, the reasons for IP change addresses, and the methods for managing them, you can take control of your network and protect your online privacy. Remember to consider the implications of a changing IP address on your various online activities and adjust your security settings accordingly. Whether you’re restarting your router, using a VPN, or contacting your ISP, you now have the knowledge to effectively manage your IP address change.
