Secure Your Connection: Understanding and Implementing a Proxy with SSL
In today’s digital landscape, online security and privacy are paramount. A crucial tool in achieving these goals is a proxy with SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). This article delves into the intricacies of proxies, SSL encryption, and how their combination enhances your online security. We’ll explore the benefits, implementation methods, and best practices for using a proxy with SSL to safeguard your data and maintain anonymity.
What is a Proxy Server?
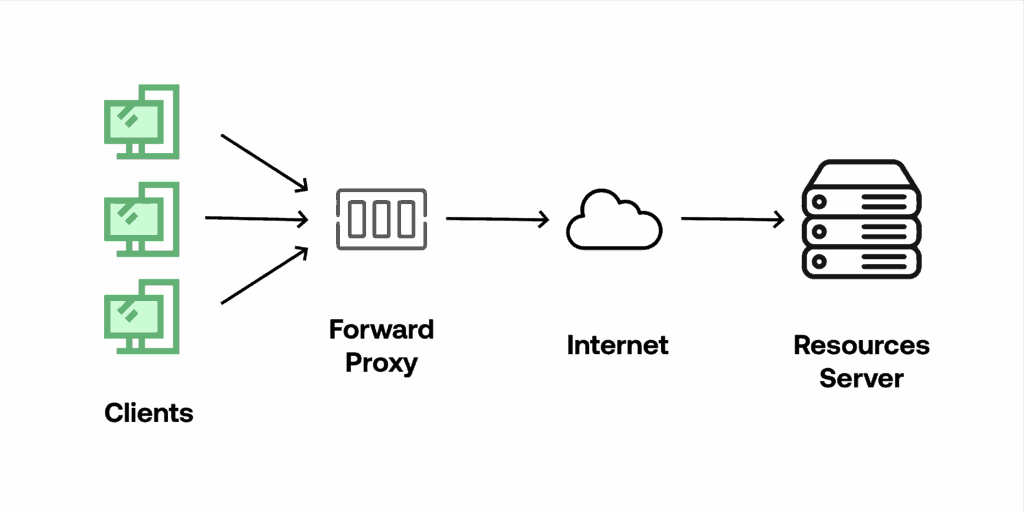
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. When you send a request to a website or online service, it first goes to the proxy server. The proxy then forwards the request to the destination server on your behalf, and subsequently relays the response back to you. This process masks your IP address, making it harder for websites to track your location and browsing habits.
- Forward Proxy: Used by clients within a network to access the internet.
- Reverse Proxy: Used by servers to protect and optimize traffic to backend servers.
Understanding SSL Encryption
SSL, now largely superseded by TLS (Transport Layer Security), is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide secure communication over a network. It encrypts data transmitted between a client (e.g., your web browser) and a server, preventing eavesdropping and tampering. The telltale sign of SSL/TLS encryption is the padlock icon in your browser’s address bar and the use of “HTTPS” in the URL.
SSL certificates are issued by Certificate Authorities (CAs) and verify the identity of the website, ensuring that you are communicating with the legitimate server and not an imposter. This is crucial for protecting sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, and personal data.
The Power of Combining a Proxy with SSL
Using a proxy with SSL provides an extra layer of security compared to using a regular proxy or SSL alone. Here’s why:
- Enhanced Privacy: The proxy masks your IP address, while SSL encrypts your data in transit. This makes it significantly harder for third parties to intercept and decipher your online activity.
- Data Protection: SSL encryption ensures that your data remains confidential, even if the proxy server itself is compromised.
- Bypassing Restrictions: In some cases, a proxy with SSL can be used to bypass geographical restrictions or censorship, as the encrypted connection makes it difficult to identify the content being accessed.
- Secure Public Wi-Fi: Using a proxy with SSL is particularly important when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks, which are often unsecured and vulnerable to eavesdropping.
Types of Proxies that Support SSL
Several types of proxies can be configured to use SSL encryption:
- HTTPS Proxies: These proxies are specifically designed to handle HTTPS traffic and automatically encrypt the connection between your device and the proxy server.
- SOCKS Proxies: SOCKS proxies are more versatile and can handle various types of traffic, including HTTPS. When used with SSL, they provide a secure tunnel for all your online activity.
- VPNs (Virtual Private Networks): While not strictly proxies, VPNs function similarly by routing your traffic through a remote server and encrypting the connection. Many VPN services use SSL/TLS encryption to secure your data.
Implementing a Proxy with SSL
Setting up a proxy with SSL typically involves the following steps:
- Choose a Proxy Service: Select a reputable proxy provider that offers SSL encryption. Consider factors like speed, reliability, server locations, and pricing.
- Configure Your Browser or Operating System: Most web browsers and operating systems allow you to configure proxy settings. Enter the proxy server’s address and port number in the appropriate settings.
- Enable SSL Encryption: Ensure that SSL encryption is enabled in your browser or proxy client. This may involve installing an SSL certificate or configuring the proxy client to use HTTPS.
- Verify the Connection: Once the proxy is configured, verify that your connection is secure by visiting a website that displays your IP address. The displayed IP address should match the proxy server’s IP address, and the connection should be encrypted (HTTPS).
Configuration Examples
Browser Configuration (Chrome)
- Go to Settings > Advanced > System > Open your computer’s proxy settings.
- Select “Manual proxy setup”.
- Enter the proxy address and port.
- Ensure “Use a proxy server” is enabled.
Command Line (cURL)
You can use cURL to test a proxy with SSL from the command line:
curl --proxy https://proxy.example.com:443 https://www.example.comBenefits of Using a Proxy with SSL
The advantages of using a proxy with SSL are numerous and cater to a variety of needs:
- Enhanced Security: Protects your data from eavesdropping and tampering, especially on public Wi-Fi.
- Improved Privacy: Masks your IP address, making it harder to track your online activity.
- Access to Geo-Restricted Content: Allows you to bypass geographical restrictions and access content that may be blocked in your region.
- Increased Anonymity: Makes it more difficult for websites and online services to identify you.
- Network Performance: Some proxies can cache content, leading to faster loading times for frequently accessed websites.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
While a proxy with SSL offers significant benefits, it’s essential to be aware of potential drawbacks:
- Performance Overhead: The encryption and routing process can introduce some latency, potentially slowing down your internet connection.
- Cost: Many reputable proxy services charge a fee for their services.
- Trust: You are entrusting your data to the proxy provider, so it’s crucial to choose a reputable and trustworthy service.
- Complexity: Configuring a proxy with SSL can be technically challenging for some users.
Best Practices for Using a Proxy with SSL
To maximize the benefits and minimize the risks of using a proxy with SSL, follow these best practices:
- Choose a Reputable Provider: Research and select a proxy provider with a proven track record of security and reliability.
- Use Strong Passwords: Protect your proxy account with a strong and unique password.
- Keep Your Software Up-to-Date: Ensure that your browser, operating system, and proxy client are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Monitor Your Traffic: Regularly monitor your network traffic for any suspicious activity.
- Read the Privacy Policy: Understand how the proxy provider handles your data and what measures they take to protect your privacy.
Use Cases for Proxies with SSL
Here are some common scenarios where using a proxy with SSL can be beneficial:
- Protecting Sensitive Data: When accessing sensitive information like bank accounts or medical records, a proxy with SSL can help protect your data from interception.
- Bypassing Censorship: In countries with strict internet censorship, a proxy with SSL can be used to access blocked websites and online services.
- Web Scraping: Web scraping activities can be made more anonymous and less likely to be blocked by using a proxy with SSL.
- Online Gaming: Gamers can use a proxy with SSL to reduce lag and improve their online gaming experience, while also protecting their IP address from DDoS attacks.
- Research and Development: Researchers and developers can use a proxy with SSL to test their applications and websites from different geographical locations.
The Future of Proxies and SSL
As online security threats continue to evolve, the importance of proxies and SSL encryption will only increase. We can expect to see further advancements in proxy technology, such as improved performance, enhanced security features, and greater ease of use. Similarly, SSL/TLS encryption protocols will continue to evolve to address emerging vulnerabilities and provide even stronger protection for online data. The combination of a robust proxy with SSL will remain a cornerstone of online security and privacy for years to come.
Conclusion
A proxy with SSL is a powerful tool for enhancing your online security and privacy. By masking your IP address and encrypting your data, it provides an extra layer of protection against eavesdropping, tampering, and tracking. While there are potential drawbacks to consider, the benefits of using a proxy with SSL far outweigh the risks, especially when following best practices and choosing a reputable provider. Whether you’re concerned about protecting sensitive data, bypassing censorship, or simply maintaining your anonymity online, a proxy with SSL can be an invaluable asset.
Consider the advantages and disadvantages outlined in this article and determine if implementing a proxy with SSL is right for your needs. Keep your online activities safe and secure by leveraging the power of a well-configured proxy with SSL.
[See also: Understanding VPN Protocols]
[See also: How to Choose the Right Proxy Server]
[See also: The Importance of Encryption in Online Security]
