Proxy Defined: Understanding Its Function, Benefits, and Security Implications
In the ever-evolving landscape of the internet, understanding the tools and technologies that facilitate our online experience is crucial. One such tool, often operating behind the scenes, is the proxy server. When discussing “proxy defined,” we are referring to a server that acts as an intermediary between a client (like your computer) and another server (like a website). This intermediary role has significant implications for security, privacy, and performance. This article delves into the core functionality of a proxy defined, exploring its various types, benefits, and potential drawbacks. Understanding the nuances of a proxy defined allows users to make informed decisions about their online activities and security.
What is a Proxy Server? A Detailed Explanation
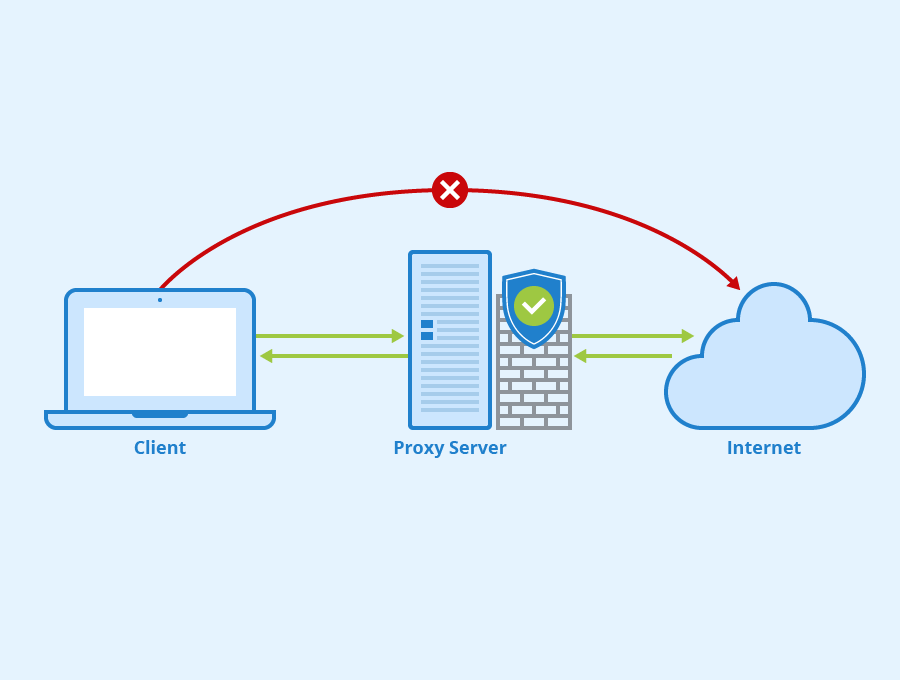
At its most basic, a proxy defined is a computer system or router that functions as a relay between a client and a server. Instead of connecting directly to the server, the client connects to the proxy defined, which then forwards the client’s request to the server. The server then sends the response back to the proxy defined, which, in turn, forwards it to the client. This intermediary process masks the client’s IP address, providing a layer of anonymity. The concept of a proxy defined is fundamental to understanding how internet traffic can be managed and secured.
The Basic Functionality of a Proxy Defined
The primary function of a proxy defined is to act as an intermediary. This role enables several crucial capabilities:
- IP Address Masking: A proxy defined hides the client’s actual IP address, making it difficult for websites and online services to track the client’s location and identity.
- Content Filtering: Organizations can use a proxy defined to block access to certain websites or types of content, enforcing internet usage policies.
- Caching: A proxy defined can store copies of frequently accessed web pages, reducing bandwidth usage and improving response times for subsequent requests.
- Security: By acting as a gateway, a proxy defined can protect clients from malicious websites and attacks.
Types of Proxy Servers
Not all proxies are created equal. There are several types of proxy servers, each with its own characteristics and use cases. Understanding these different types is essential to choosing the right proxy defined for your needs.
HTTP Proxies
HTTP proxies are designed specifically for handling web traffic. They work with the HTTP protocol and are commonly used for web browsing. These proxies can cache web pages, filter content, and mask IP addresses. An HTTP proxy defined is often used in corporate environments to control internet access. [See also: Corporate Network Security Best Practices]
HTTPS Proxies
HTTPS proxies are similar to HTTP proxies but offer an additional layer of security. They encrypt the traffic between the client and the proxy defined, protecting sensitive data from eavesdropping. HTTPS proxies are essential for secure online transactions and protecting personal information. This type of proxy defined ensures the data transmitted is encrypted.
SOCKS Proxies
SOCKS proxies are more versatile than HTTP and HTTPS proxies. They can handle any type of network traffic, including email, FTP, and peer-to-peer applications. SOCKS proxies operate at a lower level of the network stack, making them more flexible but potentially less secure than HTTP/HTTPS proxies. A SOCKS proxy defined is useful for applications that require a wide range of protocols.
Transparent Proxies
Transparent proxies are typically used by ISPs and organizations to intercept and redirect web traffic without the client’s knowledge. These proxies are often used for caching and content filtering but can raise privacy concerns. With a transparent proxy defined, users are often unaware their traffic is being routed through a proxy server.
Anonymous Proxies
Anonymous proxies hide the client’s IP address but identify themselves as proxies. While they provide some level of anonymity, websites can still detect that a proxy defined is being used. They offer a balance between privacy and functionality. [See also: Online Privacy Tools and Techniques]
Elite Proxies
Elite proxies, also known as high-anonymity proxies, hide both the client’s IP address and the fact that a proxy defined is being used. They provide the highest level of anonymity but can be more difficult to find and configure. An elite proxy defined is often preferred by users who require maximum privacy.
Benefits of Using a Proxy Defined
Using a proxy defined offers several benefits, ranging from improved security and privacy to enhanced performance and access to geo-restricted content.
Enhanced Security
A proxy defined can protect clients from malicious websites and attacks by acting as a gateway between the client and the internet. It can filter out harmful content and prevent direct connections to potentially dangerous servers. This added layer of security is particularly valuable for organizations and individuals concerned about online threats.
Improved Privacy
By masking the client’s IP address, a proxy defined can enhance online privacy. This makes it more difficult for websites and online services to track the client’s activities and collect personal information. For users concerned about their digital footprint, a proxy defined can be a valuable tool.
Access to Geo-Restricted Content
A proxy defined can be used to bypass geographical restrictions and access content that is not available in the client’s location. By connecting to a proxy defined in a different country, users can appear to be browsing from that location, unlocking access to region-locked websites and services.
Content Filtering and Monitoring
Organizations can use a proxy defined to filter and monitor internet traffic, enforcing internet usage policies and preventing access to inappropriate content. This is particularly useful in schools, workplaces, and other environments where responsible internet usage is important.
Load Balancing
In larger networks, a proxy defined can be used to distribute traffic across multiple servers, improving performance and preventing overload. This is especially useful for websites and applications with high traffic volumes. [See also: Load Balancing Techniques for Web Servers]
Potential Drawbacks and Security Considerations
While using a proxy defined offers several benefits, it’s essential to be aware of the potential drawbacks and security considerations.
Performance Issues
Using a proxy defined can sometimes slow down internet speeds, especially if the proxy defined is located far from the client or if it is overloaded with traffic. Choosing a reliable and well-maintained proxy defined is crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
Logging and Monitoring
Some proxy providers may log and monitor user activity, potentially compromising privacy. It’s essential to choose a proxy defined provider that has a strong privacy policy and a reputation for protecting user data. Always read the terms of service and privacy policy before using a proxy defined.
Security Risks
Using an untrusted proxy defined can expose clients to security risks, such as malware and phishing attacks. It’s crucial to choose a reputable proxy defined provider and to use caution when browsing the internet. Avoid using free or public proxies, as they are often less secure.
Compatibility Issues
Some websites and applications may not work correctly with a proxy defined. This can be due to compatibility issues or to websites actively blocking proxy defined usage. Always test the proxy defined with the websites and applications you intend to use.
Choosing the Right Proxy Defined
Selecting the appropriate proxy defined depends on your specific needs and priorities. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
Security
Prioritize security by choosing a proxy defined provider with a strong reputation and a commitment to protecting user data. Look for providers that offer encryption and other security features.
Speed
Choose a proxy defined that offers fast and reliable performance. Consider the location of the proxy defined and its network infrastructure.
Anonymity
If anonymity is a priority, choose an elite proxy defined that hides both your IP address and the fact that you are using a proxy defined.
Cost
Consider the cost of the proxy defined service. Free proxies may be tempting, but they are often less secure and reliable than paid options. Evaluate your budget and choose a proxy defined that offers the best value for your money.
Purpose
Determine the main reason for using a proxy defined. Are you trying to bypass geo-restrictions, enhance security, or improve privacy? Your answer will help you narrow down your options.
Conclusion
Understanding what a “proxy defined” means is essential for navigating the complexities of the modern internet. By acting as intermediaries, proxies offer a range of benefits, from enhanced security and privacy to access to geo-restricted content. However, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential drawbacks and security considerations when using a proxy defined. By carefully choosing a reputable provider and understanding the different types of proxies available, users can leverage the power of proxies to enhance their online experience. In conclusion, a proxy defined is a versatile tool that, when used correctly, can significantly improve your online security, privacy, and access to information.
