What a Proxy Server Does: Unveiling Its Functions and Benefits
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, understanding the intricacies of network infrastructure is paramount. One crucial component often overlooked is the proxy server. But what a proxy server does, how it functions, and why it’s essential for both individual users and large organizations are questions that warrant careful examination. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of what a proxy server does, its various functionalities, and the benefits it offers in enhancing security, privacy, and performance.
Understanding the Basics of a Proxy Server
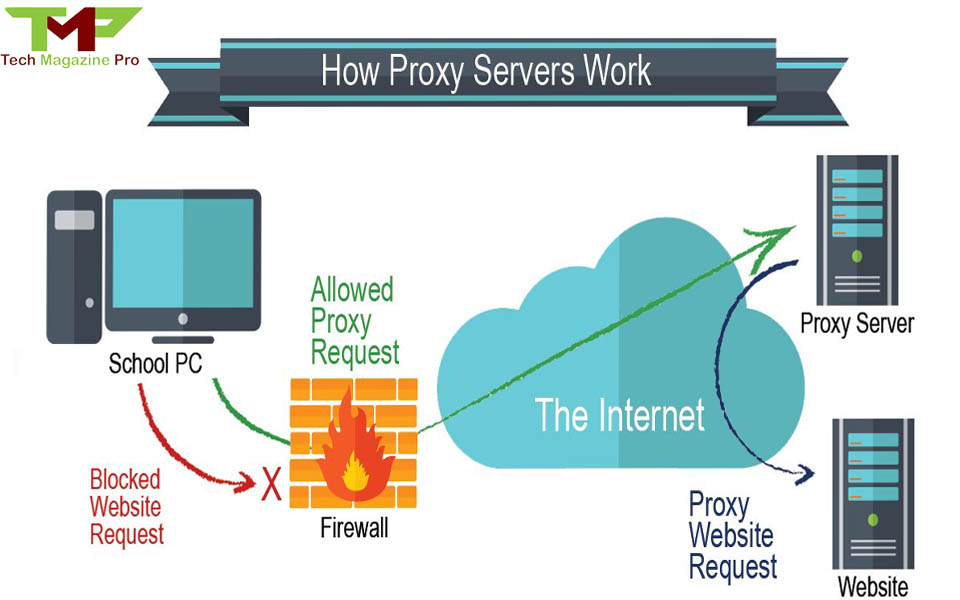
At its core, a proxy server acts as an intermediary between a user’s computer or device and the internet. Instead of directly connecting to a website or online service, the user’s request is routed through the proxy server. The proxy server then forwards the request to the destination server and relays the response back to the user. This seemingly simple process unlocks a multitude of advantages.
The Proxy Server as an Intermediary
Imagine a diplomat representing their country in a foreign land. The diplomat communicates on behalf of their nation, conveying messages and negotiating agreements. Similarly, a proxy server acts as a digital diplomat, representing the user’s computer on the internet. This indirection provides several key benefits.
Key Functions of a Proxy Server
What a proxy server does can be categorized into several key functions, each contributing to a more secure, private, and efficient online experience.
Enhanced Security
One of the primary functions of a proxy server is to enhance security. By masking the user’s IP address, the proxy server makes it more difficult for malicious actors to track the user’s online activity. This is particularly important in preventing denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and other forms of cyber threats. Furthermore, some proxy servers include built-in firewalls and malware scanners, providing an additional layer of protection against malicious content.
Organizations often use proxy servers to protect their internal networks from external threats. By routing all internet traffic through the proxy server, administrators can implement strict security policies and monitor network activity for suspicious behavior. [See also: Network Security Best Practices]
Improved Privacy
Privacy is a growing concern in the digital age. Proxy servers can help protect users’ privacy by hiding their IP address and location from websites and online services. This makes it more difficult for companies to track users’ online behavior and collect personal data. For individuals concerned about online surveillance, using a proxy server can be a valuable tool for maintaining anonymity. Some proxy servers also offer encryption, further enhancing privacy by scrambling the data transmitted between the user and the server.
Content Filtering and Access Control
Proxy servers can be configured to filter content and control access to certain websites or online services. This is particularly useful for organizations that want to restrict employees’ access to non-work-related websites or for parents who want to protect their children from inappropriate content. Content filtering can be based on keywords, website categories, or specific URLs. Access control can be used to block access to certain websites entirely or to limit access to certain features.
Caching and Bandwidth Management
Many proxy servers include caching capabilities, which can significantly improve website loading times and reduce bandwidth consumption. When a user requests a website, the proxy server checks its cache to see if a recent copy of the website is available. If it is, the proxy server serves the cached copy to the user, bypassing the need to retrieve the website from the origin server. This can result in faster loading times and reduced bandwidth usage, especially for frequently accessed websites. For organizations with limited bandwidth, caching can be a valuable tool for optimizing network performance.
Bypassing Geographical Restrictions
Some websites and online services are only available in certain geographical regions. Proxy servers can be used to bypass these restrictions by routing the user’s traffic through a server located in a different country. This allows users to access content that would otherwise be unavailable to them. For example, a user in the United States could use a proxy server located in the United Kingdom to access BBC iPlayer, a streaming service that is only available to UK residents.
Types of Proxy Servers
Not all proxy servers are created equal. There are several different types of proxy servers, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding the different types of proxy servers is essential for choosing the right one for your needs.
HTTP Proxies
HTTP proxy servers are designed specifically for handling HTTP traffic, which is the protocol used for web browsing. They are commonly used for caching web pages and filtering content. HTTP proxy servers are relatively simple to set up and use, making them a popular choice for individual users and small businesses.
HTTPS Proxies
HTTPS proxy servers are similar to HTTP proxy servers, but they also support the HTTPS protocol, which is used for secure web browsing. HTTPS proxy servers encrypt the data transmitted between the user and the server, providing an additional layer of security. They are often used by organizations that need to protect sensitive data, such as financial information or personal data.
SOCKS Proxies
SOCKS proxy servers are more versatile than HTTP and HTTPS proxy servers. They can handle any type of network traffic, including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and SMTP. SOCKS proxy servers are often used for bypassing firewalls and accessing blocked websites. They are also commonly used for online gaming and other applications that require low latency.
Transparent Proxies
Transparent proxy servers are designed to be invisible to the user. They intercept all network traffic and route it through the proxy server without the user’s knowledge. Transparent proxy servers are often used by ISPs and organizations to cache web pages and filter content. They can also be used to monitor network activity and enforce security policies.
Anonymous Proxies
Anonymous proxy servers are designed to hide the user’s IP address and location. They do not reveal the user’s IP address to the websites and online services that they access. Anonymous proxy servers are often used by individuals who want to protect their privacy and anonymity online.
Distorting Proxies
Distorting proxy servers not only hide your IP address but also provide a false one. This can make it more difficult for websites to track your location and identify you. However, some websites may block traffic from distorting proxy servers because they are often used for malicious purposes.
Choosing the Right Proxy Server
Selecting the appropriate proxy server depends on your specific requirements and priorities. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Security: If security is a top priority, choose a proxy server with built-in firewall and malware scanning capabilities.
- Privacy: If privacy is a concern, opt for an anonymous proxy server that hides your IP address and location.
- Performance: If you need to improve website loading times, select a proxy server with caching capabilities.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the proxy server is compatible with your operating system and web browser.
- Cost: Proxy servers range in price from free to hundreds of dollars per month. Choose a proxy server that fits your budget.
Potential Drawbacks of Using a Proxy Server
While proxy servers offer numerous benefits, it’s essential to acknowledge their potential drawbacks:
- Slower Connection Speeds: Routing traffic through a proxy server can sometimes introduce latency, resulting in slower connection speeds.
- Reliability Issues: Free proxy servers can be unreliable and prone to downtime.
- Security Risks: Some proxy servers may log your browsing activity or inject malware into your traffic. It’s crucial to choose a reputable proxy server provider.
Conclusion
What a proxy server does is multifaceted, offering a range of benefits from enhanced security and privacy to improved performance and access to geographically restricted content. By acting as an intermediary between the user and the internet, a proxy server provides a valuable layer of protection and control. However, it’s essential to carefully consider the different types of proxy servers and their potential drawbacks before making a decision. Whether you’re an individual user concerned about online privacy or an organization seeking to protect its network from cyber threats, understanding what a proxy server does and how it works is crucial for navigating the complexities of the digital world.
