Configuring Proxy Server Settings in Mozilla Firefox: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s interconnected world, maintaining online privacy and security is more crucial than ever. One effective method to enhance your anonymity and bypass geographical restrictions is by utilizing a proxy server. Mozilla Firefox, a widely used web browser, offers robust options for configuring proxy server Mozilla settings. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, explaining the various settings and their implications, ensuring you can navigate the internet safely and efficiently.
Understanding Proxy Servers
Before diving into the configuration process, it’s essential to understand what a proxy server is and how it functions. A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your computer and the internet. When you browse the web through a proxy, your internet traffic is routed through the proxy server, masking your IP address and location. This can be beneficial for several reasons:
- Enhanced Privacy: By hiding your IP address, a proxy server makes it more difficult for websites and advertisers to track your online activities.
- Bypassing Geographical Restrictions: Some websites and services are only available in certain regions. A proxy server can allow you to access content that would otherwise be blocked.
- Improved Security: A proxy server can add an extra layer of security by filtering malicious content and preventing direct connections between your computer and potentially harmful websites.
- Load Balancing: In some cases, proxy servers are used to distribute network traffic across multiple servers, improving performance and reliability.
Accessing Proxy Settings in Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox provides several ways to access and configure proxy server Mozilla settings. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Via the Options Menu:
- Open Mozilla Firefox.
- Click on the menu button (three horizontal lines) in the top-right corner.
- Select “Settings”.
- In the “General” panel, scroll down to the “Network Settings” section.
- Click on the “Settings…” button next to “Configure how Firefox connects to the Internet”.
- Via the `about:preferences` URL:
- Open a new tab in Firefox.
- Type `about:preferences` in the address bar and press Enter.
- Navigate to the “General” panel and follow steps 4 and 5 from the Options Menu method.
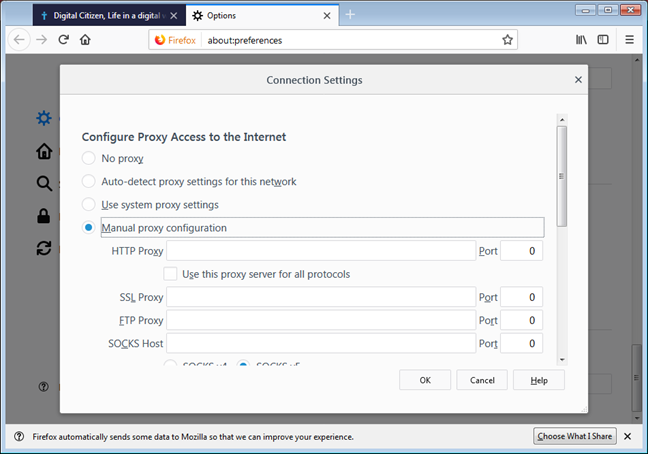
Both methods will lead you to the “Connection Settings” dialog box, where you can configure your proxy server Mozilla settings.
Configuring Proxy Server Settings
The “Connection Settings” dialog box offers several options for configuring your proxy server:
- No Proxy: This option disables the use of a proxy server. Firefox will connect directly to the internet.
- Auto-detect proxy settings for this network: This option instructs Firefox to automatically detect proxy settings from your local network configuration. This is often used in corporate environments where proxy settings are automatically distributed.
- Use system proxy settings: This option tells Firefox to use the proxy settings configured in your operating system.
- Manual proxy configuration: This option allows you to manually enter the details of your proxy server. This is the most common option for users who want to use a specific proxy server.
- Automatic proxy configuration URL: This option allows you to specify a URL that points to a Proxy Auto-Configuration (PAC) file. A PAC file is a script that determines which proxy server to use for a given URL.
Manual Proxy Configuration
If you choose the “Manual proxy configuration” option, you will need to enter the following information:
- HTTP Proxy: The hostname or IP address of the HTTP proxy server.
- Port: The port number of the HTTP proxy server.
- SSL Proxy: The hostname or IP address of the SSL (HTTPS) proxy server. This is used for secure connections.
- Port: The port number of the SSL proxy server.
- FTP Proxy: The hostname or IP address of the FTP proxy server.
- Port: The port number of the FTP proxy server.
- SOCKS Host: The hostname or IP address of the SOCKS proxy server. SOCKS proxies are more versatile than HTTP proxies and can be used for a wider range of applications.
- Port: The port number of the SOCKS proxy server.
- No Proxy for: A list of hostnames or IP addresses that should bypass the proxy server. This is useful for accessing local network resources without going through the proxy.
After entering the necessary information, click “OK” to save your proxy server Mozilla settings.
Automatic Proxy Configuration URL
If you choose the “Automatic proxy configuration URL” option, you will need to enter the URL of the PAC file. A PAC file is a JavaScript file that contains a function called `FindProxyForURL`. This function determines which proxy server to use for a given URL based on various criteria, such as the hostname, protocol, and time of day.
PAC files are often used in corporate environments to manage proxy settings centrally. They allow administrators to define complex proxy rules that can be easily updated without requiring users to manually configure their browser settings.
Types of Proxy Servers
There are several types of proxy servers, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- HTTP Proxies: These are the most common type of proxy server. They are designed to handle HTTP traffic and are typically used for web browsing.
- HTTPS Proxies: These are similar to HTTP proxies but are used for secure connections (HTTPS). They encrypt the traffic between your computer and the proxy server, providing an extra layer of security.
- SOCKS Proxies: These are more versatile than HTTP proxies and can handle a wider range of applications. They operate at a lower level of the network stack and can be used for any type of traffic.
- Transparent Proxies: These proxies do not modify the HTTP headers, and the client is unaware that a proxy is being used. These are often used by ISPs or network administrators to cache web content and improve performance.
- Anonymous Proxies: These proxies hide your IP address but do not identify themselves as proxies. They provide a moderate level of anonymity.
- Elite Proxies: These proxies hide your IP address and identify themselves as proxies, providing the highest level of anonymity.
Finding a Reliable Proxy Server
Finding a reliable proxy server can be challenging, as many free proxy servers are unreliable or even malicious. It’s important to choose a proxy server from a reputable provider and to exercise caution when using free proxy servers. Here are some tips for finding a reliable proxy server:
- Research the provider: Before using a proxy server, research the provider and read reviews from other users. Look for providers with a good reputation and a history of providing reliable service.
- Consider a paid proxy service: Paid proxy services typically offer better performance, reliability, and security than free proxy servers. They also tend to have fewer users, which can result in faster connection speeds.
- Test the proxy server: Before relying on a proxy server, test it to make sure it’s working properly. You can use online tools to check your IP address and verify that it’s being hidden by the proxy server.
- Be wary of free proxy servers: Free proxy servers are often unreliable and may be used for malicious purposes. They may also be overloaded with users, resulting in slow connection speeds.
Troubleshooting Proxy Server Issues
If you encounter problems with your proxy server Mozilla settings, here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Check your proxy settings: Make sure that you have entered the correct proxy server address and port number. Double-check for typos or other errors.
- Clear your browser cache and cookies: Sometimes, cached data can interfere with proxy server connections. Clearing your browser cache and cookies can resolve these issues.
- Disable browser extensions: Some browser extensions can interfere with proxy server connections. Try disabling your extensions to see if that resolves the problem.
- Check your firewall settings: Make sure that your firewall is not blocking connections to the proxy server.
- Contact your proxy server provider: If you are still having problems, contact your proxy server provider for assistance.
Security Considerations
While proxy servers can enhance your online privacy and security, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks involved. Some proxy servers may log your internet activity, while others may inject malicious content into your web traffic. Here are some security considerations to keep in mind when using a proxy server:
- Choose a reputable proxy server provider: As mentioned earlier, it’s important to choose a proxy server from a reputable provider with a good track record.
- Use a secure connection: When possible, use an HTTPS proxy to encrypt the traffic between your computer and the proxy server.
- Be careful about entering sensitive information: Avoid entering sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card numbers, while using a proxy server.
- Monitor your internet activity: Keep an eye on your internet activity and watch out for any suspicious behavior.
Understanding and properly configuring proxy server Mozilla settings is a valuable skill for anyone concerned about online privacy and security. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively use proxy servers to enhance your anonymity, bypass geographical restrictions, and protect yourself from online threats. Always prioritize security and choose reputable providers to ensure a safe and reliable browsing experience. [See also: How to Choose the Right Proxy Server for Your Needs]
