Define Web Crawler: Understanding the Mechanics of Internet Indexing
In the vast and ever-expanding digital landscape, the ability to efficiently navigate and index the web is paramount. This is where the concept of a web crawler comes into play. But what exactly is a web crawler? At its core, a web crawler, also known as a spider or bot, is an automated program designed to systematically browse the World Wide Web. Its primary function is to collect information, index content, and follow links, thereby creating a comprehensive map of the internet. This article will delve into the intricacies of web crawlers, exploring their functionalities, applications, and the crucial role they play in modern search engines and data aggregation.
The Anatomy of a Web Crawler
To fully define web crawler, it’s essential to break down its components and understand how they interact. A typical web crawler operates using a set of well-defined steps:
- Seeding: The crawler begins with a list of URLs to visit, known as the ‘seed’ URLs. These initial URLs act as the starting point for the crawling process.
- Fetching: The crawler retrieves the HTML content associated with each URL. This involves sending an HTTP request to the web server and receiving the server’s response.
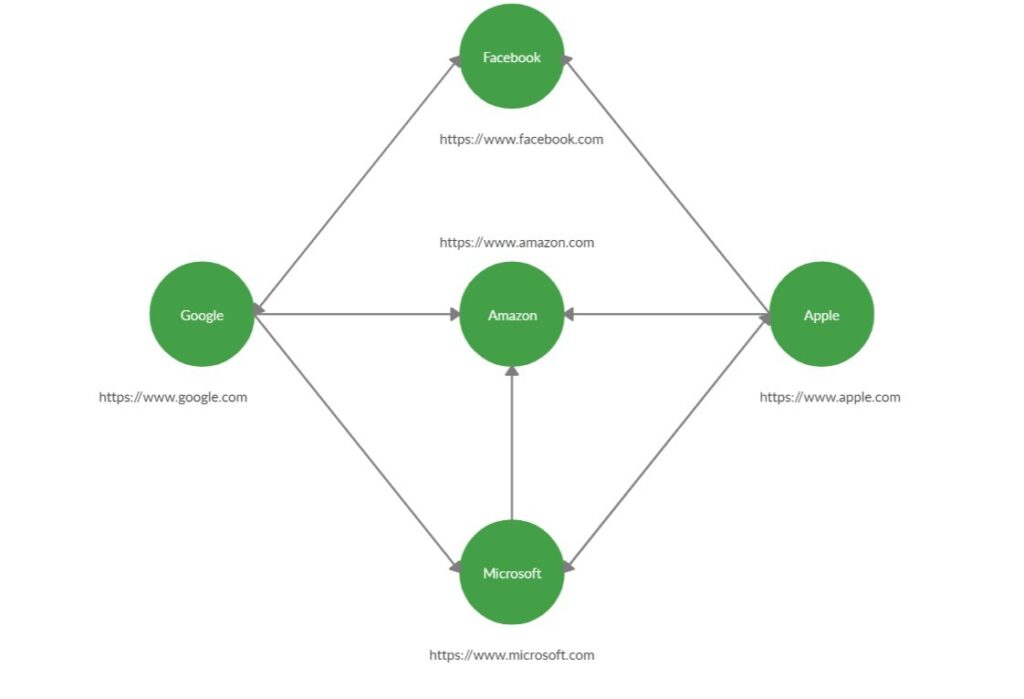
- Parsing: Once the HTML content is retrieved, the crawler parses the content to extract relevant information, such as text, images, and, most importantly, links to other URLs.
- Link Extraction: The crawler identifies and extracts all the hyperlinks present within the parsed HTML content. These links are then added to a queue of URLs to be visited in subsequent iterations.
- Indexing: The extracted information, including text, metadata, and links, is indexed and stored in a database. This index serves as the foundation for search engine algorithms, allowing users to quickly find relevant information.
- Policy Enforcement: Throughout the crawling process, the crawler adheres to a set of policies and rules, such as respecting robots.txt files and avoiding overloading web servers with excessive requests.
How Web Crawlers Work in Practice
Imagine a web crawler starting its journey from a single webpage. It downloads that page, analyzes its content, and identifies all the links pointing to other pages. These new links are then added to a queue, and the crawler systematically visits each of them, repeating the process. This continuous cycle of fetching, parsing, link extraction, and indexing allows the web crawler to traverse the vast network of interconnected webpages, gradually building a comprehensive index of the web.
Consider, for example, a news aggregator like Google News. It uses web crawlers to constantly scan news websites for the latest articles. The crawlers extract the headlines, summaries, and links to the full articles, which are then indexed and presented to users in a personalized news feed.
The Importance of Web Crawlers
Web crawlers are fundamental to the functioning of the modern internet. They are the invisible engines that power search engines, enabling users to find information quickly and efficiently. Without web crawlers, search engines would be unable to index the vast amount of content available online, rendering them virtually useless. Furthermore, web crawlers are essential for various other applications, including:
- Data Mining: Extracting valuable data from websites for research, analysis, and business intelligence.
- Web Archiving: Creating archives of websites to preserve historical information.
- Monitoring: Tracking changes to websites, such as price updates, news articles, or legal notices.
- SEO Audits: Analyzing website structure and content to identify areas for improvement in search engine optimization.
Challenges and Considerations
While web crawlers are powerful tools, they also present several challenges and considerations. One of the primary challenges is dealing with the sheer scale and complexity of the web. The internet contains billions of webpages, and the content is constantly changing. Web crawlers must be able to efficiently manage this vast amount of data and adapt to the dynamic nature of the web.
Another important consideration is ethical crawling. Web crawlers must respect website owners’ wishes and avoid overloading servers with excessive requests. This is typically achieved by adhering to the robots.txt protocol, which allows website owners to specify which parts of their site should not be crawled. Additionally, crawlers should implement politeness policies, such as limiting the number of requests per second and avoiding crawling during peak hours.
Furthermore, web crawlers must be able to handle various types of content, including dynamic websites, multimedia files, and password-protected pages. This requires sophisticated parsing and rendering techniques.
Types of Web Crawlers
Not all web crawlers are created equal. Different types of crawlers are designed for specific purposes and employ different techniques. Some common types of web crawlers include:
- Focused Crawlers: These crawlers target specific topics or websites. They are designed to efficiently collect information related to a particular subject area.
- Incremental Crawlers: These crawlers periodically revisit previously crawled pages to detect changes and update the index. They are essential for keeping search engine results fresh and accurate.
- Deep Web Crawlers: These crawlers attempt to access content that is not readily available through standard search engines, such as databases and password-protected pages.
- Mobile Crawlers: Designed to specifically crawl and index mobile websites, ensuring optimal search results for mobile users.
Web Crawlers and SEO
The relationship between web crawlers and Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is crucial. SEO is the practice of optimizing a website to improve its visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). Web crawlers play a central role in this process by indexing website content and providing search engines with the information they need to rank websites. [See also: SEO Best Practices for 2024]
To ensure that a website is properly indexed by web crawlers, it is essential to follow SEO best practices, such as:
- Creating high-quality, relevant content: Search engines prioritize websites that provide valuable and informative content to users.
- Using descriptive titles and meta descriptions: These elements help search engines understand the content of a webpage and display relevant snippets in search results.
- Building a clear and logical website structure: A well-organized website is easier for web crawlers to navigate and index.
- Using internal linking: Linking to other pages within a website helps web crawlers discover and index all of the content.
- Creating a robots.txt file: This file allows website owners to control which parts of their site are crawled by search engines.
- Submitting a sitemap to search engines: A sitemap provides search engines with a list of all the pages on a website, making it easier for them to index the content.
The Future of Web Crawling
As the internet continues to evolve, web crawlers will need to adapt to new technologies and challenges. One of the key trends in web crawling is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). AI-powered crawlers can automatically learn and adapt to new website structures and content types, making them more efficient and effective. [See also: The Impact of AI on SEO]
Another trend is the growing importance of mobile crawling. With the increasing use of mobile devices, search engines are prioritizing mobile-friendly websites in their search results. Web crawlers must be able to accurately assess the mobile-friendliness of websites to ensure that they are properly indexed.
Finally, the rise of the Semantic Web is also impacting web crawling. The Semantic Web aims to make web content more machine-readable by adding metadata and structured data to webpages. Web crawlers can use this metadata to extract more meaningful information from websites and improve the accuracy of search results. Properly defining a web crawler is thus more important than ever.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a web crawler is a fundamental tool for navigating and indexing the vast expanse of the internet. These automated programs systematically browse the web, collecting information, extracting links, and building a comprehensive index that powers search engines and various other applications. Understanding how web crawlers work is essential for anyone involved in SEO, data mining, or web development. As the internet continues to evolve, web crawlers will play an increasingly important role in shaping the way we access and interact with information online. Defining the purpose and function of a web crawler is crucial for understanding the modern internet. The efficiency and accuracy of these web crawlers directly impact the user experience and the ability to find relevant information in the digital world. The future of web crawling lies in adapting to new technologies and challenges, ensuring that these vital tools remain effective and ethical in their operation. Understanding how to define web crawler and its function is very important.
