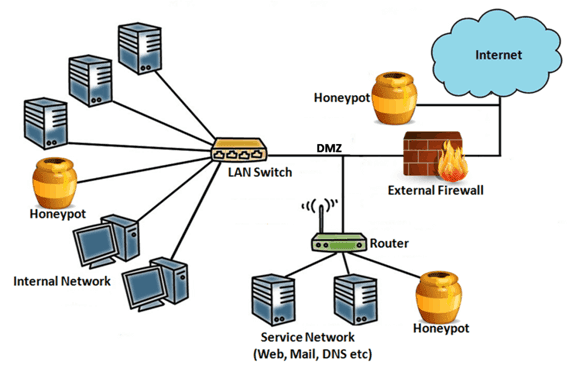
Honey Pot Trap: Understanding Cyber Deception and Network Security
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, organizations are constantly seeking innovative ways to defend their networks against malicious actors. One such technique, the honey pot trap, offers a unique approach to threat detection and intelligence gathering. A honey pot trap is essentially a decoy system designed to lure attackers, allowing security teams to observe their methods, gather valuable data, and ultimately, protect real assets. This article delves into the intricacies of honey pot traps, exploring their types, benefits, implementation strategies, and the ethical considerations surrounding their use.
What is a Honey Pot Trap?
A honey pot trap is a security resource whose value lies in being probed, attacked, or compromised. Unlike production systems that are designed to provide legitimate services, a honey pot trap serves no functional purpose other than to attract malicious activity. By mimicking real systems and services, honey pot traps can effectively deceive attackers into believing they have found a vulnerable target. This deception allows security professionals to gain insights into the attacker’s motives, techniques, and tools.
Key Characteristics of Honey Pot Traps
- Deception: Honey pots are designed to appear as legitimate targets, enticing attackers to interact with them.
- Monitoring: All interactions with the honey pot are closely monitored and logged, providing valuable data about attacker behavior.
- Resource Consumption: Honey pots should not consume significant resources or impact the performance of production systems.
- Containment: Honey pots must be carefully contained to prevent attackers from using them to launch attacks against other systems.
Types of Honey Pot Traps
Honey pot traps come in various forms, each designed to emulate different types of systems and services. The type of honey pot deployed will depend on the specific security goals and the types of threats the organization is trying to detect.
Low-Interaction Honey Pots
Low-interaction honey pot traps simulate only a limited number of services or applications. They are relatively easy to deploy and maintain, making them a popular choice for organizations with limited resources. Examples include emulating open ports or vulnerable services. When an attacker interacts with a low-interaction honey pot, the information gathered is typically limited to the attacker’s IP address and the type of exploit attempted.
High-Interaction Honey Pots
High-interaction honey pot traps, on the other hand, provide a more realistic environment for attackers. They often involve deploying full-fledged operating systems and applications, allowing attackers to interact with the system as if it were a real production server. High-interaction honey pots can provide a wealth of information about attacker behavior, including the tools they use, the commands they execute, and the data they attempt to steal. However, they are also more complex to deploy and maintain, and they pose a greater risk of being compromised and used to launch attacks against other systems. Careful monitoring and containment are crucial when using high-interaction honey pot traps.
Client Honey Pots
Unlike server-side honey pot traps that passively wait for attackers to connect, client honey pot traps actively seek out malicious servers or websites. These honey pot traps are typically deployed on virtual machines or sandboxes and are used to analyze the behavior of malware or phishing attacks. When a client honey pot encounters a malicious server, it logs the interaction and provides valuable information about the attacker’s infrastructure and tactics.
Benefits of Using Honey Pot Traps
Implementing honey pot traps can offer numerous benefits to an organization’s security posture:
- Early Threat Detection: Honey pots can detect attacks that might otherwise go unnoticed by traditional security measures. Because they have no legitimate purpose, any interaction with a honey pot is inherently suspicious.
- Intelligence Gathering: Honey pots provide valuable insights into attacker motives, techniques, and tools. This information can be used to improve security defenses and prevent future attacks.
- Resource Diversion: By diverting attackers to honey pots, organizations can protect their real assets from harm. This can be particularly useful in situations where resources are limited.
- False Positive Reduction: Honey pots generate very few false positives, as any interaction with them is likely to be malicious. This can help security teams focus their attention on genuine threats.
- Training and Education: Honey pots can be used as a training tool for security professionals, allowing them to gain hands-on experience in analyzing attacker behavior.
Implementing a Honey Pot Trap
Deploying a honey pot trap requires careful planning and execution. Here are some key considerations:
Define Clear Objectives
Before deploying a honey pot, it’s important to define clear objectives. What types of threats are you trying to detect? What information are you hoping to gather? Defining clear objectives will help you choose the right type of honey pot and configure it appropriately.
Choose the Right Type of Honey Pot
As mentioned earlier, there are various types of honey pot traps, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choose the type of honey pot that best aligns with your objectives and resources. For example, if you are looking to detect automated attacks, a low-interaction honey pot may be sufficient. However, if you are interested in analyzing the behavior of sophisticated attackers, a high-interaction honey pot may be necessary.
Configure the Honey Pot Realistically
To effectively deceive attackers, a honey pot trap must be configured realistically. This means emulating real systems and services, using realistic data, and avoiding obvious signs that the system is a decoy. The more realistic the honey pot, the more likely it is to attract attackers and provide valuable information. The honey pot trap must appear as a legitimate target.
Monitor and Analyze Interactions
The value of a honey pot trap lies in the data it generates. It’s essential to monitor all interactions with the honey pot and analyze the logs to identify attacker behavior, tools, and techniques. This information can be used to improve security defenses and prevent future attacks. [See also: Incident Response Planning]
Contain the Honey Pot
To prevent attackers from using the honey pot to launch attacks against other systems, it’s crucial to contain the honey pot within a controlled environment. This can be achieved through the use of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures. Proper containment is essential for minimizing the risk associated with deploying high-interaction honey pots. The honey pot trap should be isolated.
Ethical Considerations
While honey pot traps can be a valuable security tool, it’s important to consider the ethical implications of their use. Some critics argue that honey pots are a form of entrapment, as they intentionally deceive attackers into committing crimes. Others raise concerns about privacy, as honey pots may collect personal information about attackers. It’s crucial to use honey pot traps responsibly and in accordance with all applicable laws and regulations.
Transparency and Disclosure
Some organizations choose to disclose the presence of honey pot traps in their network security policies. This can help to deter attackers and demonstrate a commitment to ethical security practices. However, disclosure may also reduce the effectiveness of the honey pots, as attackers may be less likely to interact with them if they know they are being monitored.
Data Privacy
When deploying honey pot traps, it’s important to consider data privacy implications. Avoid collecting unnecessary personal information about attackers, and ensure that any data collected is stored securely and used only for legitimate security purposes. Adhere to all applicable data privacy laws and regulations.
Conclusion
Honey pot traps are a powerful tool for enhancing network security and gathering valuable intelligence about attacker behavior. By deceiving attackers and diverting them to decoy systems, organizations can protect their real assets and gain insights into the latest threats. However, it’s essential to implement honey pot traps carefully and ethically, taking into account the potential risks and ethical considerations. With proper planning and execution, honey pot traps can be a valuable addition to any organization’s security arsenal. Understanding the nuances of a honey pot trap is key to effective cybersecurity defense.
