How to Execute a Python Script in Windows: A Comprehensive Guide
Python, a versatile and widely-used programming language, finds applications in various domains, from web development to data science. Understanding how to execute a Python script in Windows is fundamental for anyone looking to leverage Python’s capabilities on this operating system. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of different methods to run your Python code, ensuring you can choose the most suitable approach for your specific needs. We’ll cover everything from the command line to IDEs, and even scheduling tasks.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the execution methods, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
- Python Installation: Download and install the latest version of Python from the official website (python.org). Make sure to add Python to your system’s PATH environment variable during installation. This allows you to run Python from any directory in the command prompt.
- Text Editor or IDE: You’ll need a text editor or Integrated Development Environment (IDE) to write and save your Python scripts. Popular options include Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, PyCharm, and Notepad++.
Methods to Execute a Python Script in Windows
There are several ways to execute a Python script in Windows. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on your workflow and requirements.
Using the Command Prompt (CMD)
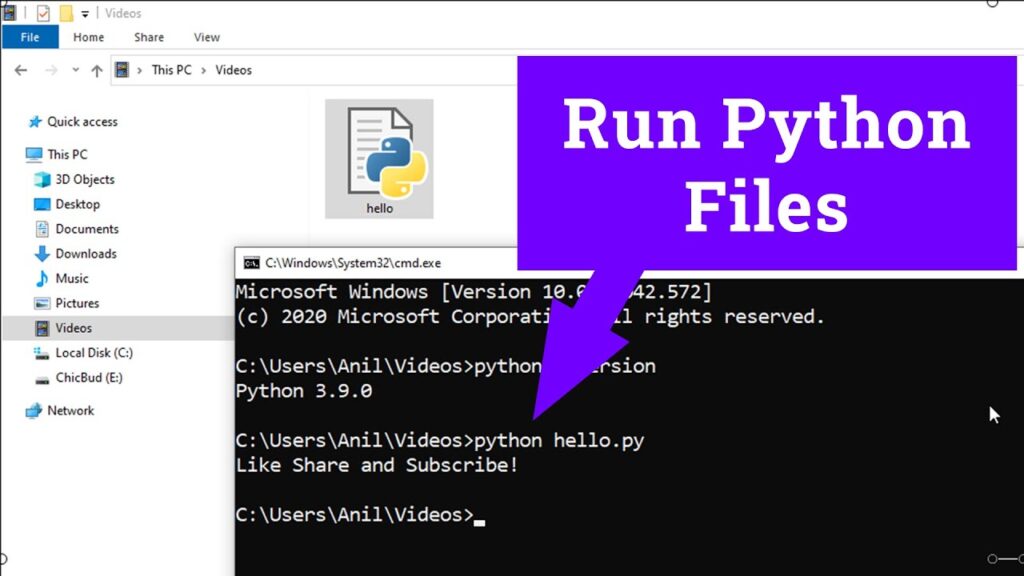
The command prompt is a powerful tool for executing commands directly on your operating system. It’s a straightforward way to execute a Python script in Windows.
- Open the Command Prompt: Press the Windows key, type “cmd,” and press Enter.
- Navigate to the Script’s Directory: Use the
cdcommand to navigate to the directory where your Python script is located. For example, if your script is inC:UsersYourNameDocumentsPythonScripts, typecd C:UsersYourNameDocumentsPythonScriptsand press Enter. - Execute the Script: Type
python your_script_name.py(replaceyour_script_name.pywith the actual name of your script) and press Enter. The Python interpreter will then execute your script.
This method is ideal for quick tests and running simple scripts. It requires minimal setup and provides direct feedback in the command prompt window.
Using PowerShell
PowerShell is a more advanced command-line shell and scripting language for Windows. Similar to CMD, it can be used to execute a Python script in Windows. While both can run Python scripts, PowerShell offers more powerful scripting capabilities and object-based management.
- Open PowerShell: Press the Windows key, type “powershell,” and press Enter.
- Navigate to the Script’s Directory: Use the
cdcommand to navigate to the directory containing your Python script. The syntax is the same as in CMD. - Execute the Script: Type
python your_script_name.py(replaceyour_script_name.pywith the actual name of your script) and press Enter. Alternatively, you can simply type the script name,your_script_name.py, and PowerShell will automatically use the associated Python interpreter.
PowerShell is useful for automating tasks and managing system configurations, making it a suitable choice for more complex scripting scenarios. It is another effective method to execute a Python script in Windows.
Using Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
IDEs provide a comprehensive environment for developing and executing Python scripts in Windows. They offer features such as code completion, debugging tools, and project management capabilities.
PyCharm
PyCharm is a popular IDE specifically designed for Python development. It simplifies the process to execute a Python script in Windows.
- Open PyCharm: Launch the PyCharm application.
- Open Your Script: Open your Python script in PyCharm by navigating to
File > Openand selecting your script file. - Run the Script: Right-click anywhere in the script editor and select “Run ‘your_script_name'” or click the green “Run” button in the top right corner.
PyCharm offers advanced debugging features, making it easier to identify and fix errors in your code. Its integrated environment streamlines the development process.
Visual Studio Code (VS Code)
VS Code is a versatile and lightweight code editor that supports Python development through extensions. It’s a good option if you want to execute a Python script in Windows but prefer a less resource-intensive IDE.
- Install the Python Extension: Open VS Code and install the Python extension from the VS Code Marketplace.
- Open Your Script: Open your Python script in VS Code by navigating to
File > Open Fileand selecting your script file. - Run the Script: Right-click anywhere in the script editor and select “Run Python File in Terminal” or press
Ctrl+Shift+P(orCmd+Shift+Pon macOS) and type “Run Python File in Terminal.”
VS Code’s flexibility and extensive extension ecosystem make it a powerful tool for Python development. It provides a good balance between features and performance, allowing you to efficiently execute a Python script in Windows.
Double-Clicking the Script File
If Python is correctly installed and associated with the .py extension, you can simply double-click the Python script file in Windows Explorer to execute a Python script in Windows. This method is convenient for running scripts quickly, but it may not be suitable for scripts that require command-line arguments or user input.
Note: If the script executes too quickly and the output disappears, you can add input() at the end of your script to pause the execution and keep the console window open until you press Enter.
Creating a Batch File
A batch file is a simple text file containing a series of commands that can be executed in the command prompt. You can create a batch file to execute a Python script in Windows with specific configurations.
- Create a New Text File: Open Notepad or any text editor and create a new file.
- Add the Execution Command: Type the command to execute your Python script, such as
python your_script_name.py. - Save the File: Save the file with a
.batextension (e.g.,run_script.bat). - Execute the Batch File: Double-click the batch file to execute the Python script.
Batch files are useful for automating repetitive tasks and running scripts with predefined arguments. They provide a convenient way to execute a Python script in Windows without manually typing the command each time.
Scheduling Python Scripts with Task Scheduler
Windows Task Scheduler allows you to schedule tasks to run automatically at specific times or intervals. This is useful for automating Python scripts that need to be executed regularly. To execute a Python script in Windows using Task Scheduler:
- Open Task Scheduler: Press the Windows key, type “task scheduler,” and press Enter.
- Create a Basic Task: In the Task Scheduler window, click “Create Basic Task” in the right-hand pane.
- Name and Describe the Task: Enter a name and description for the task and click “Next.”
- Choose a Trigger: Select when you want the task to start (e.g., Daily, Weekly, Monthly) and click “Next.”
- Configure the Trigger: Specify the details for the selected trigger (e.g., time of day, days of the week) and click “Next.”
- Choose an Action: Select “Start a program” and click “Next.”
- Specify the Program and Arguments:
- Program/script: Type
python(or the full path to your Python executable if it’s not in your PATH). - Add arguments: Type the full path to your Python script (e.g.,
C:UsersYourNameDocumentsPythonScriptsyour_script_name.py). - Start in (optional): Type the directory where your Python script is located (e.g.,
C:UsersYourNameDocumentsPythonScripts).
Click “Next.”
- Program/script: Type
- Review and Finish: Review the task details and click “Finish.”
Task Scheduler is ideal for automating tasks that need to run regularly, such as data backups, report generation, or system maintenance scripts. It provides a reliable way to execute a Python script in Windows without manual intervention.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When trying to execute a Python script in Windows, you might encounter some common issues:
- ‘python’ is not recognized as an internal or external command: This error indicates that Python is not added to your system’s PATH environment variable. Reinstall Python and ensure you select the option to add Python to PATH during installation. Alternatively, manually add the Python installation directory to your PATH.
- SyntaxError: invalid syntax: This error indicates a syntax error in your Python code. Review your code carefully and correct any syntax errors. Using an IDE can help identify these errors more easily.
- ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘module_name’: This error indicates that a required Python module is not installed. Install the module using
pip install module_namein the command prompt or PowerShell. - Script executes too quickly and the output disappears: Add
input()at the end of your script to pause the execution and keep the console window open until you press Enter.
Best Practices
Here are some best practices for executing Python scripts in Windows:
- Use Virtual Environments: Create virtual environments for each project to isolate dependencies and avoid conflicts between different projects. You can create a virtual environment using
python -m venv myenvand activate it usingmyenvScriptsactivate. - Write Clear and Concise Code: Follow Python’s style guide (PEP 8) to write clean and readable code. This makes it easier to debug and maintain your scripts.
- Use Logging: Implement logging in your scripts to track execution progress and identify potential issues. The
loggingmodule in Python provides a flexible way to log messages to files or the console. - Handle Errors Gracefully: Use
try...exceptblocks to handle exceptions and prevent your scripts from crashing. Provide informative error messages to help diagnose issues.
Conclusion
Executing a Python script in Windows can be achieved through various methods, each offering unique advantages. Whether you prefer the command line, an IDE, or task scheduling, understanding these techniques empowers you to efficiently run your Python code. By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this guide, you can ensure smooth execution and effective troubleshooting of your Python scripts. Remember to choose the method that best suits your workflow and project requirements to maximize your productivity. With the right approach, you can effectively execute a Python script in Windows and leverage the full potential of this powerful programming language.
[See also: Python Scripting for System Administration]
[See also: Automating Tasks with Python and Windows Task Scheduler]
[See also: Debugging Python Code in VS Code]
