How to Extract Information from a Website: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s data-driven world, the ability to extract information from a website is a crucial skill for researchers, businesses, and individuals alike. Whether you’re gathering market intelligence, conducting academic research, or simply automating tasks, understanding how to effectively extract information from a website can save you time and provide valuable insights. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the techniques, tools, and ethical considerations involved in web scraping and data extraction.
Understanding Web Scraping
Web scraping, also known as web harvesting or web data extraction, is the process of automatically collecting information from the World Wide Web. It typically involves using software to simulate human browsing and extract specific data points from web pages. The extracted data can then be stored in a structured format, such as a spreadsheet or database, for further analysis.
Why Extract Information from a Website?
There are numerous reasons why someone might want to extract information from a website. Some common use cases include:
- Market Research: Monitoring competitor pricing, product offerings, and marketing strategies.
- Lead Generation: Collecting contact information of potential customers.
- News Aggregation: Gathering news articles from various sources.
- Academic Research: Collecting data for social science, linguistics, or other research projects.
- Real Estate Analysis: Tracking property listings and market trends.
- Financial Analysis: Monitoring stock prices, economic indicators, and financial news.
Methods for Extracting Information
Several methods can be used to extract information from a website, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Manual Copy-Pasting
The simplest method is to manually copy and paste information from a website into a document or spreadsheet. While this approach is suitable for small-scale data collection, it is time-consuming and impractical for large datasets.
Using Browser Extensions
Several browser extensions, such as Web Scraper and Data Miner, can simplify the process of extracting information from a website. These extensions allow you to select specific elements on a web page and extract their content into a CSV or other structured format. They are generally easier to use than programming-based methods but may be limited in their capabilities.
Programming with Web Scraping Libraries
For more complex data extraction tasks, programming with web scraping libraries is often the most effective approach. Popular libraries include:
- Python (Beautiful Soup, Scrapy): Python is a versatile programming language with powerful libraries like Beautiful Soup and Scrapy that are well-suited for web scraping. Beautiful Soup is a parsing library that makes it easy to navigate HTML and XML documents, while Scrapy is a comprehensive web scraping framework that provides tools for crawling websites, extracting data, and storing the results. [See also: Python Web Scraping Tutorial]
- JavaScript (Cheerio, Puppeteer): JavaScript can be used to scrape dynamic websites that rely heavily on JavaScript to render content. Cheerio is a fast and flexible parsing library similar to jQuery, while Puppeteer is a Node library that allows you to control headless Chrome or Chromium instances, enabling you to interact with websites as a real user would.
- Java (Jsoup): Jsoup is a Java library for parsing HTML documents. It provides a convenient API for extracting data and manipulating HTML elements.
Using APIs
Many websites provide APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow developers to access their data in a structured format. Using an API is often the preferred method for extracting information from a website, as it is typically more reliable and efficient than web scraping. However, not all websites offer APIs, and those that do may have usage restrictions or require authentication.
The Web Scraping Process
The process of extracting information from a website typically involves the following steps:
- Identify the Target Website: Determine the website you want to scrape and the specific data you need to extract.
- Inspect the Website’s Structure: Analyze the HTML structure of the website to identify the elements containing the data you want to extract. Use browser developer tools (e.g., Chrome DevTools) to examine the HTML code and CSS selectors.
- Write the Scraping Code: Write code using a programming language and web scraping library to fetch the HTML content of the website and extract the desired data.
- Handle Dynamic Content: If the website uses JavaScript to render content, use a headless browser or other techniques to execute the JavaScript code and extract the dynamically generated content.
- Store the Extracted Data: Store the extracted data in a structured format, such as a CSV file, database, or JSON file.
- Clean and Process the Data: Clean and process the extracted data to remove any inconsistencies or errors. This may involve removing duplicates, converting data types, and standardizing formatting.
- Automate the Scraping Process: Schedule the scraping script to run automatically on a regular basis to keep the data up-to-date.
Ethical Considerations and Legal Issues
While extracting information from a website can be a valuable tool, it is important to be aware of the ethical and legal considerations involved. Web scraping can put a strain on a website’s resources, and it may violate the website’s terms of service or copyright laws. Before scraping a website, it is important to:
- Review the Website’s Terms of Service: Check the website’s terms of service to see if web scraping is permitted. Many websites explicitly prohibit web scraping in their terms of service.
- Check the robots.txt File: The robots.txt file is a text file that tells web crawlers which parts of a website should not be accessed. Respect the instructions in the robots.txt file.
- Avoid Overloading the Website: Limit the rate at which you send requests to the website to avoid overloading its servers. Implement delays between requests and use caching to reduce the number of requests.
- Respect Copyright Laws: Be aware of copyright laws and avoid scraping content that is protected by copyright.
- Identify Yourself: Include a user-agent string in your scraping requests that identifies your scraper. This allows website administrators to contact you if they have any concerns.
Tools and Technologies for Web Scraping
Several tools and technologies can be used to extract information from a website. Here’s a breakdown:
Programming Languages and Libraries
- Python: With libraries like Beautiful Soup, Scrapy, and Selenium, Python is a favorite for web scraping due to its simplicity and extensive ecosystem. The combination of ease-of-use and powerful libraries makes extracting information from a website using Python a common choice.
- JavaScript: Libraries like Cheerio and Puppeteer enable scraping of dynamic content rendered by JavaScript. Puppeteer, in particular, is invaluable for interacting with websites that heavily rely on client-side rendering.
- Java: Jsoup provides a simple API for parsing and manipulating HTML, making it suitable for Java-based scraping projects.
Web Scraping Frameworks
- Scrapy (Python): A powerful and flexible framework for building web scrapers. It handles crawling, data extraction, and data processing efficiently.
Cloud-Based Scraping Services
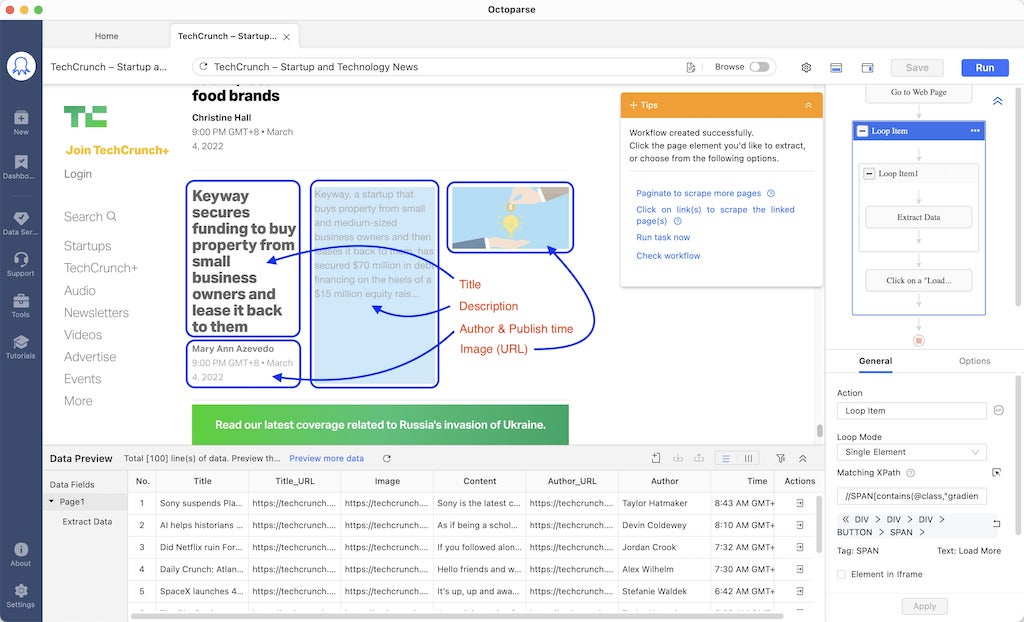
- ParseHub: A visual web scraping tool that allows you to extract data without writing code.
- Apify: A cloud platform for web scraping and automation. It provides tools for building, deploying, and managing web scrapers.
- Bright Data: Offers a range of web scraping solutions, including proxies, data collection tools, and managed scraping services.
Advanced Techniques
For more complex web scraping scenarios, consider these advanced techniques:
Handling CAPTCHAs
CAPTCHAs (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) are designed to prevent bots from accessing websites. To handle CAPTCHAs, you can use CAPTCHA solving services that automatically solve CAPTCHAs for you. [See also: How to Bypass CAPTCHAs in Web Scraping]
Using Proxies
Proxies can be used to hide your IP address and avoid being blocked by websites. Rotating proxies is a technique that involves using a pool of proxies and switching between them to further reduce the risk of being blocked. When you extract information from a website at scale, using proxies is nearly essential.
Handling Dynamic Content
For websites that use JavaScript to render content, you need to use a headless browser or other techniques to execute the JavaScript code and extract the dynamically generated content. Puppeteer and Selenium are popular choices for handling dynamic content. Effectively extracting information from a website that relies on JavaScript requires a different approach than static HTML pages.
Best Practices for Web Scraping
To ensure that your web scraping efforts are successful and ethical, follow these best practices:
- Be Respectful: Respect the website’s terms of service and robots.txt file.
- Limit Your Request Rate: Avoid overloading the website’s servers by limiting the rate at which you send requests.
- Use Caching: Cache the HTML content of websites to reduce the number of requests.
- Handle Errors Gracefully: Implement error handling to gracefully handle unexpected errors or changes in the website’s structure.
- Monitor Your Scraper: Monitor your scraper to ensure that it is working correctly and that it is not causing any problems for the website.
Conclusion
Extracting information from a website is a powerful tool that can be used for a variety of purposes. By understanding the techniques, tools, and ethical considerations involved, you can effectively collect data and gain valuable insights. Remember to always respect the website’s terms of service and robots.txt file, and to avoid overloading its servers. With the right approach, you can extract information from a website efficiently and ethically, unlocking a wealth of data for your research, business, or personal projects. Learning how to properly extract information from a website is a valuable asset in today’s digital landscape.
