Mastering Inspect Element on Firefox: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of web development and digital troubleshooting, the Inspect Element tool within web browsers like Firefox stands as an indispensable asset. This powerful feature allows users to delve into the underlying code of any webpage, providing insights into its structure, styling, and behavior. Whether you’re a seasoned developer debugging complex issues or a curious user wanting to understand how a website is built, mastering Inspect Element on Firefox is a skill that can significantly enhance your understanding of the internet. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the various functionalities of Inspect Element, offering practical examples and tips to maximize its potential.
Understanding the Basics of Inspect Element
Inspect Element is a built-in developer tool available in Firefox (and most other modern browsers). It essentially provides a real-time view of a webpage’s HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code. This allows you to examine and modify these elements directly within the browser, without affecting the actual website files on the server. Think of it as a temporary sandbox where you can experiment with changes and see their immediate impact.
Accessing Inspect Element on Firefox
There are several ways to access Inspect Element in Firefox:
- Right-Click Method: Right-click anywhere on the webpage and select “Inspect” or “Inspect Element” from the context menu. This will open the developer tools panel, usually at the bottom or side of the browser window. The specific element you right-clicked on will be highlighted in the HTML code.
- Keyboard Shortcut: Press Ctrl+Shift+I (Windows/Linux) or Cmd+Opt+I (macOS) to open the developer tools directly.
- Firefox Menu: Navigate to the Firefox menu (usually three horizontal lines in the top-right corner), then select “Web Developer” and then “Inspector.”
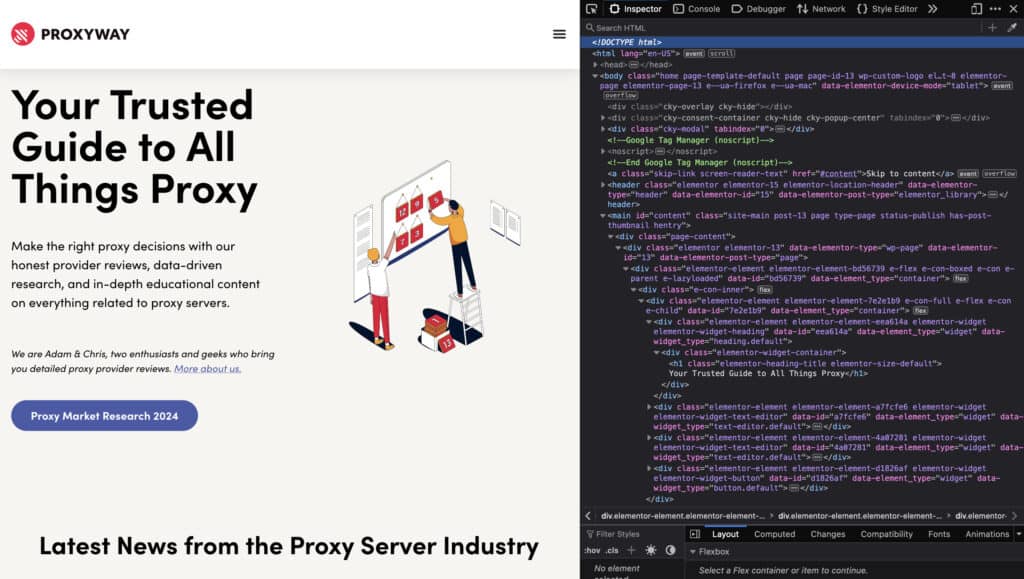
Once the developer tools panel is open, you’ll see several tabs, including “Inspector,” “Console,” “Debugger,” “Network,” and more. The “Inspector” tab is where you’ll find the Inspect Element functionality.
Exploring the Inspector Tab
The Inspector tab is the heart of Inspect Element. It displays the HTML structure of the webpage in a hierarchical tree. You can expand and collapse elements to navigate through the code. When you select an element in the HTML tree, the corresponding element on the webpage is highlighted.
Navigating the HTML Tree
The HTML tree represents the Document Object Model (DOM) of the webpage. The DOM is a programming interface for HTML and XML documents. It represents the page so that programs can change the document structure, style, and content. Inspect Element allows you to traverse this tree and examine each element’s attributes and properties.
You can use the arrow keys (up, down, left, right) to navigate the HTML tree. The left arrow key collapses an expanded element, while the right arrow key expands a collapsed element.
Inspecting Element Styles (CSS)
When you select an element in the HTML tree, the “Styles” panel on the right side of the Inspector tab displays the CSS rules that apply to that element. This panel shows the CSS rules defined in external stylesheets, inline styles, and browser default styles. You can see which rules are being applied and which are being overridden.
The Styles panel is incredibly useful for debugging CSS issues. You can quickly identify conflicting styles, incorrect values, and missing rules. You can also edit the CSS rules directly in the panel to see how changes affect the element’s appearance. These changes are temporary and only visible to you.
Modifying HTML and CSS in Real-Time
One of the most powerful features of Inspect Element is the ability to modify HTML and CSS directly in the browser. This allows you to experiment with different designs and layouts without having to edit the actual website files.
To edit an HTML element, simply double-click on it in the HTML tree. You can then type in your changes and press Enter to apply them. To edit a CSS rule, click on the value or property in the Styles panel. You can then type in your changes and press Enter to apply them.
These changes are temporary and will be lost when you refresh the page. However, they are incredibly useful for testing different ideas and debugging issues.
Advanced Features of Inspect Element
Beyond the basic functionality, Inspect Element offers several advanced features that can further enhance your web development and troubleshooting capabilities.
The Console Tab
The Console tab is a powerful tool for debugging JavaScript code and logging messages. It allows you to execute JavaScript commands directly in the browser and see the results. You can also use the console to view error messages, warnings, and other information generated by the webpage.
To use the console, simply type in a JavaScript command and press Enter. The result of the command will be displayed in the console. You can also use the `console.log()` function to print messages to the console from your JavaScript code.
The Debugger Tab
The Debugger tab allows you to step through JavaScript code line by line, set breakpoints, and inspect variables. This is an invaluable tool for identifying and fixing bugs in your JavaScript code.
To use the debugger, you need to open the JavaScript file in the Debugger tab. You can then set breakpoints by clicking in the gutter next to the line numbers. When the JavaScript code reaches a breakpoint, the debugger will pause execution and allow you to inspect the current state of the program.
The Network Tab
The Network tab allows you to monitor the network requests made by the webpage. This can be useful for identifying slow-loading resources, debugging API calls, and optimizing website performance. You can see the details of each request, including the URL, status code, headers, and response body.
The Network tab also allows you to filter the requests by type (e.g., HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images). This can help you quickly identify specific types of resources that are causing issues.
Using Inspect Element for Responsive Design Testing
Inspect Element can also be used to test the responsiveness of a website on different screen sizes. Firefox’s Responsive Design Mode allows you to simulate different devices and resolutions, ensuring your website looks good on all devices. To access Responsive Design Mode, open Inspect Element, and look for the toggle device icon (usually next to the element picker) or use Ctrl+Shift+M (or Cmd+Shift+M on macOS).
This mode allows you to select predefined device sizes or enter custom dimensions. You can also simulate different network conditions (e.g., slow 3G) to see how your website performs under different circumstances.
Practical Examples of Using Inspect Element
To illustrate the power of Inspect Element, let’s look at some practical examples:
- Changing Text on a Webpage: Suppose you want to see how a different headline would look on a webpage. Simply right-click on the headline, select “Inspect,” and then double-click on the text in the HTML tree. You can then type in your new headline and press Enter to see the changes.
- Adjusting CSS Styles: Imagine you want to change the color of a button on a webpage. Right-click on the button, select “Inspect,” and then find the CSS rule that defines the button’s color in the Styles panel. You can then click on the color value and enter a new color to see how it looks.
- Debugging JavaScript Errors: If you encounter an error message on a webpage, open the Console tab to see the details of the error. The console will often provide information about the line of code that caused the error, which can help you track down the bug.
- Analyzing Network Performance: If a webpage is loading slowly, open the Network tab to see which resources are taking the longest to load. This can help you identify bottlenecks and optimize your website’s performance.
Tips and Tricks for Using Inspect Element Effectively
Here are some tips and tricks to help you use Inspect Element more effectively:
- Use the Element Picker: The Element Picker allows you to quickly select an element on the webpage by clicking on it. This can be much faster than navigating the HTML tree manually. To activate the Element Picker, click on the icon that looks like a mouse cursor over a rectangle in the top-left corner of the Inspector tab.
- Search for Elements: You can use the search bar in the Inspector tab to quickly find specific elements in the HTML tree. Simply type in a keyword or CSS selector, and the Inspector will highlight the matching elements.
- Use Breakpoints: Breakpoints are essential for debugging JavaScript code. Use them liberally to pause execution at key points in your code and inspect the current state of the program.
- Learn CSS Selectors: A good understanding of CSS selectors will make it much easier to navigate the HTML tree and find the specific elements you’re looking for.
- Experiment and Explore: The best way to learn Inspect Element is to experiment and explore its various features. Don’t be afraid to try different things and see what happens.
Conclusion
Inspect Element on Firefox is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance your web development and troubleshooting skills. By understanding its various features and functionalities, you can gain valuable insights into the inner workings of webpages and quickly identify and fix issues. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or a curious user, mastering Inspect Element is a skill that will undoubtedly prove useful in the digital age. [See also: Debugging JavaScript in Firefox] [See also: Optimizing Website Performance] So, dive in, experiment, and unlock the full potential of this invaluable tool. The ability to effectively use Inspect Element is a crucial skill for anyone working with or interested in web development. It allows for quick analysis, debugging, and experimentation, ultimately leading to better websites and a deeper understanding of web technologies.
