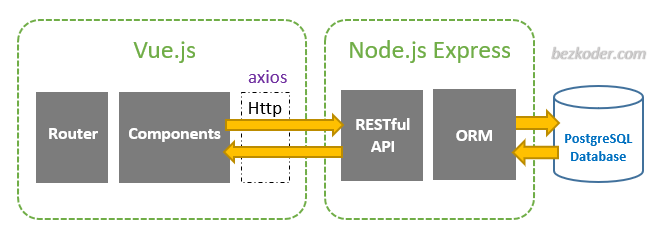
Mastering Node.js with PostgreSQL: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s data-driven world, building robust and scalable applications requires a powerful combination of technologies. Node.js, with its non-blocking, event-driven architecture, has become a popular choice for building server-side applications. PostgreSQL, a powerful, open-source relational database system, is renowned for its reliability, data integrity, and advanced features. Integrating Node PostgreSQL allows developers to create high-performance applications capable of handling complex data requirements.
This comprehensive guide explores the synergy between Node PostgreSQL, offering insights into setting up a development environment, connecting to a PostgreSQL database, performing CRUD operations, and implementing best practices for building scalable and secure applications. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting your journey, this article provides the knowledge and practical examples to effectively leverage Node PostgreSQL in your projects.
Setting Up Your Development Environment
Before diving into code, it’s crucial to have a properly configured development environment. This involves installing Node.js, npm (Node Package Manager), and PostgreSQL.
Installing Node.js and npm
Node.js can be downloaded from the official Node.js website (nodejs.org). The installation process is straightforward and includes npm by default. Verify the installation by running the following commands in your terminal:
node -v
npm -vThese commands should display the installed versions of Node.js and npm respectively.
Installing PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL can be installed using various package managers, depending on your operating system. For example, on macOS, you can use Homebrew:
brew install postgresqlOn Ubuntu/Debian, you can use apt:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contribAfter installation, ensure the PostgreSQL server is running. You can typically start the server using:
pg_ctl -D /usr/local/var/postgres startAdjust the path to your PostgreSQL data directory as needed. You’ll also need to create a database and user for your application. This can be done using the `psql` command-line tool.
Connecting Node.js to PostgreSQL
To connect your Node.js application to a PostgreSQL database, you’ll need the `pg` package. Install it using npm:
npm install pgHere’s a basic example of how to connect to a PostgreSQL database using the `pg` package:
const { Pool } = require('pg');
const pool = new Pool({
user: 'your_user',
host: 'localhost',
database: 'your_database',
password: 'your_password',
port: 5432,
});
pool.query('SELECT NOW()', (err, res) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
} else {
console.log(res.rows[0]);
}
pool.end();
});Replace `’your_user’`, `’your_database’`, and `’your_password’` with your actual PostgreSQL credentials. This code establishes a connection to the database and executes a simple query to retrieve the current timestamp.
Using Connection Pooling
Connection pooling is crucial for improving the performance and scalability of your application. Instead of creating a new connection for each request, connection pooling reuses existing connections, reducing the overhead of establishing new connections. The `pg` package provides a built-in connection pooling mechanism through the `Pool` class.
Performing CRUD Operations with Node PostgreSQL
CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations are fundamental to any database-driven application. Here’s how to perform these operations using Node PostgreSQL.
Creating Data (INSERT)
To insert data into a PostgreSQL table, use the `INSERT` statement. For example:
const query = 'INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES ($1, $2)';
const values = ['John Doe', 'john.doe@example.com'];
pool.query(query, values, (err, res) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
} else {
console.log('User inserted successfully');
}
});Reading Data (SELECT)
To retrieve data from a PostgreSQL table, use the `SELECT` statement. For example:
const query = 'SELECT * FROM users';
pool.query(query, (err, res) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
} else {
console.log(res.rows);
}
});Updating Data (UPDATE)
To update data in a PostgreSQL table, use the `UPDATE` statement. For example:
const query = 'UPDATE users SET email = $1 WHERE id = $2';
const values = ['new.email@example.com', 1];
pool.query(query, values, (err, res) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
} else {
console.log('User updated successfully');
}
});Deleting Data (DELETE)
To delete data from a PostgreSQL table, use the `DELETE` statement. For example:
const query = 'DELETE FROM users WHERE id = $1';
const values = [1];
pool.query(query, values, (err, res) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
} else {
console.log('User deleted successfully');
}
});Implementing Best Practices for Node PostgreSQL
To build scalable and secure applications using Node PostgreSQL, it’s essential to follow best practices.
Parameterization and Preventing SQL Injection
Always use parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection vulnerabilities. Parameterized queries ensure that user inputs are treated as data rather than executable code. The examples above demonstrate the use of parameterized queries.
Error Handling
Implement robust error handling to gracefully handle database errors. This includes logging errors, providing informative error messages to users, and implementing retry mechanisms for transient errors.
Transaction Management
Use transactions to ensure data consistency and integrity. Transactions allow you to group multiple database operations into a single atomic unit. If any operation within the transaction fails, the entire transaction is rolled back, preventing partial updates.
pool.connect((err, client, done) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
return;
}
client.query('BEGIN', (err) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
return done(err);
}
client.query('INSERT INTO table1 (data) VALUES ($1)', ['value1'], (err) => {
if (err) {
client.query('ROLLBACK', (err) => {
return done(err);
});
} else {
client.query('INSERT INTO table2 (data) VALUES ($1)', ['value2'], (err) => {
if (err) {
client.query('ROLLBACK', (err) => {
return done(err);
});
} else {
client.query('COMMIT', (err) => {
if (err) {
return done(err);
}
done();
});
}
});
}
});
});
});Connection Pooling Configuration
Properly configure the connection pool to optimize performance. Adjust the `max`, `min`, and `idleTimeoutMillis` parameters based on your application’s needs. Monitor the connection pool metrics to identify potential bottlenecks.
Asynchronous Operations
Leverage asynchronous operations to avoid blocking the event loop. Use `async/await` or Promises to handle asynchronous database operations efficiently. This ensures that your application remains responsive and scalable.
Data Validation
Implement data validation on both the client-side and server-side to prevent invalid data from being stored in the database. This includes validating data types, formats, and constraints.
Advanced Node PostgreSQL Techniques
Beyond the basics, Node PostgreSQL offers advanced techniques to enhance your application’s capabilities.
Using ORMs (Object-Relational Mappers)
ORMs like Sequelize and Knex.js provide a higher-level abstraction over raw SQL queries. They simplify database interactions and improve code maintainability. ORMs allow you to interact with the database using JavaScript objects, reducing the need to write SQL code directly.
Implementing Database Migrations
Database migrations allow you to manage changes to your database schema in a controlled and repeatable manner. Tools like Knex.js and Sequelize provide migration capabilities to automate the process of applying schema changes.
Working with JSON Data
PostgreSQL supports storing and querying JSON data natively. You can use the `jsonb` data type to store JSON documents efficiently and perform complex queries using JSON operators and functions. Node PostgreSQL makes it easy to interact with JSON data in your application.
Real-time Data with WebSockets
Combine Node PostgreSQL with WebSockets to build real-time applications. Use PostgreSQL’s LISTEN/NOTIFY feature to receive notifications when data changes and push updates to connected clients via WebSockets. This allows you to build interactive and responsive applications that reflect real-time data changes.
Conclusion
Node PostgreSQL provides a powerful and flexible platform for building modern web applications. By understanding the fundamentals of connecting to a PostgreSQL database, performing CRUD operations, and implementing best practices, you can create scalable, secure, and high-performance applications. Explore advanced techniques such as using ORMs, implementing database migrations, and working with JSON data to further enhance your application’s capabilities. Embrace the power of Node PostgreSQL and unlock the potential of your data-driven applications. This comprehensive guide should provide a solid foundation for your Node PostgreSQL endeavors. Remember to always prioritize security and performance when working with databases. By following these guidelines, you’ll be well-equipped to build robust and reliable applications using Node PostgreSQL.
[See also: Setting up a Secure Node.js API with PostgreSQL]
[See also: Optimizing PostgreSQL Performance for Node.js Applications]
