Mastering Web Automation: A Deep Dive into Puppeteer Python API
In the rapidly evolving landscape of web development and testing, automation has become an indispensable tool. Among the various automation frameworks available, the combination of Puppeteer and Python offers a powerful and versatile solution. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the Puppeteer Python API, covering its features, benefits, implementation, and practical applications. We’ll delve into how this dynamic duo empowers developers and testers to streamline workflows, enhance efficiency, and achieve unparalleled precision in web automation tasks.
What is Puppeteer?
Puppeteer is a Node.js library developed by Google’s Chrome team. It provides a high-level API to control headless (or headful) Chrome or Chromium instances. Essentially, it allows you to automate browser actions programmatically, simulating user interactions such as clicking buttons, filling forms, navigating pages, and extracting data. Originally built for testing Chrome extensions, Puppeteer has evolved into a general-purpose web automation tool.
Why Python with Puppeteer?
While Puppeteer is inherently a Node.js library, Python developers can leverage its capabilities through the Puppeteer Python API, specifically the pyppeteer library. This combination brings together the robust automation features of Puppeteer with the simplicity and versatility of Python. Python’s extensive ecosystem of libraries and frameworks makes it an ideal choice for building complex automation workflows, data analysis pipelines, and web scraping applications. Using the Puppeteer Python API allows you to perform the same actions as the Node.js version, all within a Python environment.
Key Features of the Puppeteer Python API (Pyppeteer)
- Headless and Headful Automation: Run browser automation in headless mode (without a GUI) for faster execution or in headful mode to visually observe the automation process.
- Page Navigation: Programmatically navigate to different URLs, handle redirects, and manage browser history.
- Element Interaction: Interact with web elements, including clicking buttons, filling forms, selecting dropdown options, and submitting data.
- JavaScript Execution: Inject and execute JavaScript code within the browser context, enabling advanced manipulation of web pages.
- Screenshot and PDF Generation: Capture screenshots of web pages or generate PDF documents from web content.
- Network Interception: Intercept and modify network requests and responses, allowing for testing of API interactions and performance optimization.
- Data Extraction: Extract data from web pages using CSS selectors or XPath expressions.
- Asynchronous Operations: Handle asynchronous operations efficiently using Python’s
asynciolibrary.
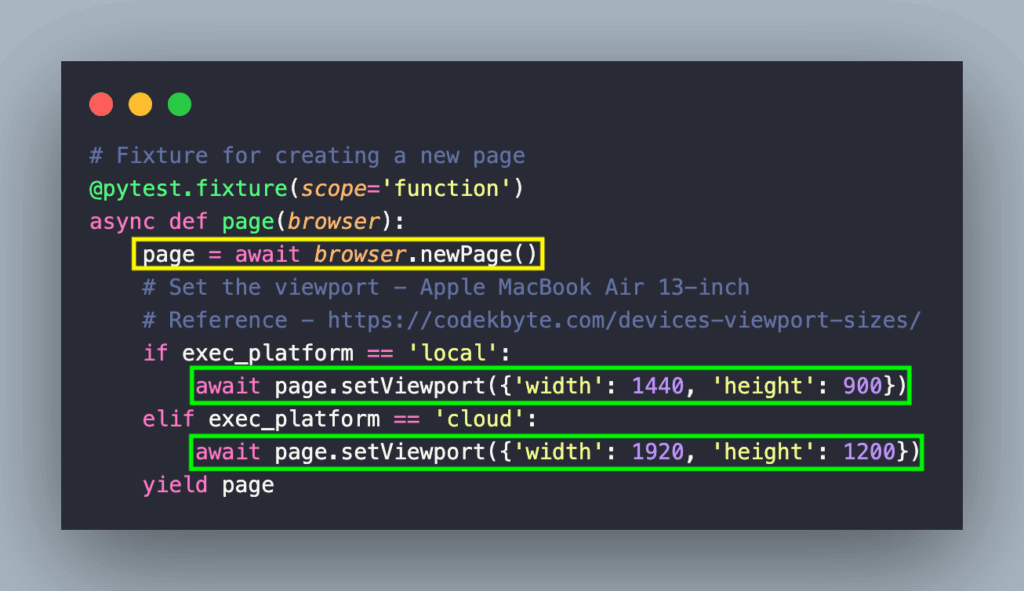
Setting Up the Puppeteer Python API (Pyppeteer)
Before you can start using the Puppeteer Python API, you need to install the pyppeteer library and its dependencies. Follow these steps:
Install Pyppeteer
Use pip, the Python package installer, to install pyppeteer:
pip install pyppeteerInstall Chromium
Pyppeteer automatically downloads and installs a compatible version of Chromium during the first execution. Alternatively, you can specify the path to an existing Chromium installation.
Basic Example
Here’s a simple example of using the Puppeteer Python API to navigate to a website and take a screenshot:
import asyncio
from pyppeteer import launch
async def main():
browser = await launch()
page = await browser.newPage()
await page.goto('https://www.example.com')
await page.screenshot({'path': 'example.png'})
await browser.close()
asyncio.get_event_loop().run_until_complete(main())
Advanced Usage of the Puppeteer Python API
The Puppeteer Python API offers a wide range of advanced features for complex web automation tasks. Let’s explore some of them.
Handling Forms
Filling out forms is a common task in web automation. Here’s how to use the Puppeteer Python API to fill out a form and submit it:
import asyncio
from pyppeteer import launch
async def main():
browser = await launch()
page = await browser.newPage()
await page.goto('https://example.com/contact')
await page.type('#name', 'John Doe')
await page.type('#email', 'john.doe@example.com')
await page.type('#message', 'This is a test message.')
await page.click('#submit')
await page.waitForNavigation()
print('Form submitted successfully!')
await browser.close()
asyncio.get_event_loop().run_until_complete(main())
Web Scraping
The Puppeteer Python API is also useful for web scraping. Here’s an example of extracting data from a table:
import asyncio
from pyppeteer import launch
async def main():
browser = await launch()
page = await browser.newPage()
await page.goto('https://example.com/data')
data = await page.evaluate('''()
=> {
const table = document.querySelector('table');
const rows = Array.from(table.querySelectorAll('tr'));
return rows.map(row => {
const cells = Array.from(row.querySelectorAll('td'));
return cells.map(cell => cell.innerText);
});
}
''')
print(data)
await browser.close()
asyncio.get_event_loop().run_until_complete(main())
Network Interception
Network interception allows you to monitor and modify network requests and responses. This is useful for testing API interactions and performance optimization. Here’s an example:
import asyncio
from pyppeteer import launch
async def main():
browser = await launch()
page = await browser.newPage()
await page.setRequestInterception(True)
page.on('request', request => {
if request.url.endswith('.png'):
request.abort()
else:
request.continue_()
})
await page.goto('https://example.com')
await page.screenshot({'path': 'example.png'})
await browser.close()
asyncio.get_event_loop().run_until_complete(main())
Best Practices for Using the Puppeteer Python API
- Use Async/Await: Leverage Python’s
asynciolibrary for efficient handling of asynchronous operations. - Handle Errors: Implement robust error handling to gracefully manage unexpected situations.
- Use CSS Selectors: Use CSS selectors for efficient and reliable element selection.
- Wait for Elements: Use
page.waitForSelector()orpage.waitForNavigation()to ensure elements are loaded before interacting with them. - Minimize Browser Instances: Reuse browser instances to reduce overhead and improve performance.
- Clean Up Resources: Always close the browser instance after completing your automation tasks.
Use Cases for Puppeteer Python API
The Puppeteer Python API is suitable for a wide range of use cases, including:
- Automated Testing: Automate UI tests to ensure the quality and reliability of web applications.
- Web Scraping: Extract data from web pages for data analysis, research, or competitive intelligence.
- PDF Generation: Generate PDF documents from web content for reporting, archiving, or documentation purposes.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor the performance of web applications by measuring page load times and other metrics.
- Task Automation: Automate repetitive tasks such as form filling, data entry, and report generation.
Alternatives to Puppeteer Python API
While Puppeteer Python API is a powerful tool, there are several alternatives to consider, depending on your specific needs and requirements:
- Selenium: A widely used web automation framework that supports multiple programming languages and browsers.
- Playwright: A newer automation framework developed by Microsoft that offers similar features to Puppeteer.
- Beautiful Soup: A Python library for parsing HTML and XML documents, primarily used for web scraping.
- Scrapy: A Python framework for building web scrapers and crawlers.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When using the Puppeteer Python API, you may encounter some common issues. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Chromium Not Found: Ensure that Chromium is installed and that Pyppeteer can find it.
- Element Not Found: Use
page.waitForSelector()to wait for the element to load before interacting with it. - Navigation Timeout: Increase the navigation timeout if the page takes too long to load.
- Asynchronous Errors: Use
asyncio.gather()to handle multiple asynchronous operations concurrently.
Conclusion
The Puppeteer Python API, powered by pyppeteer, provides a robust and versatile solution for web automation. Its ability to control headless or headful Chrome instances, combined with Python’s simplicity and extensive ecosystem, makes it an ideal choice for developers and testers seeking to streamline workflows, enhance efficiency, and achieve unparalleled precision in their automation tasks. From automated testing to web scraping and PDF generation, the Puppeteer Python API empowers users to tackle a wide range of challenges with ease and flexibility. By understanding its key features, implementing best practices, and exploring its advanced capabilities, you can unlock the full potential of this dynamic duo and elevate your web automation skills to new heights. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting out, the Puppeteer Python API is a valuable tool to have in your arsenal.
[See also: Web Scraping with Python: A Comprehensive Guide]
[See also: Automating Browser Tasks with Selenium and Python]
[See also: Introduction to Headless Browsers for Web Testing]
