Proxy Examples: Understanding Their Use Cases and Benefits
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, understanding the nuances of online security and privacy is paramount. One crucial tool in achieving this is the proxy server. This article delves into various proxy examples, exploring their functionalities, benefits, and diverse applications across different sectors. From enhancing online security to bypassing geographical restrictions, proxies offer a multifaceted solution for both individual users and organizations.
What is a Proxy Server?
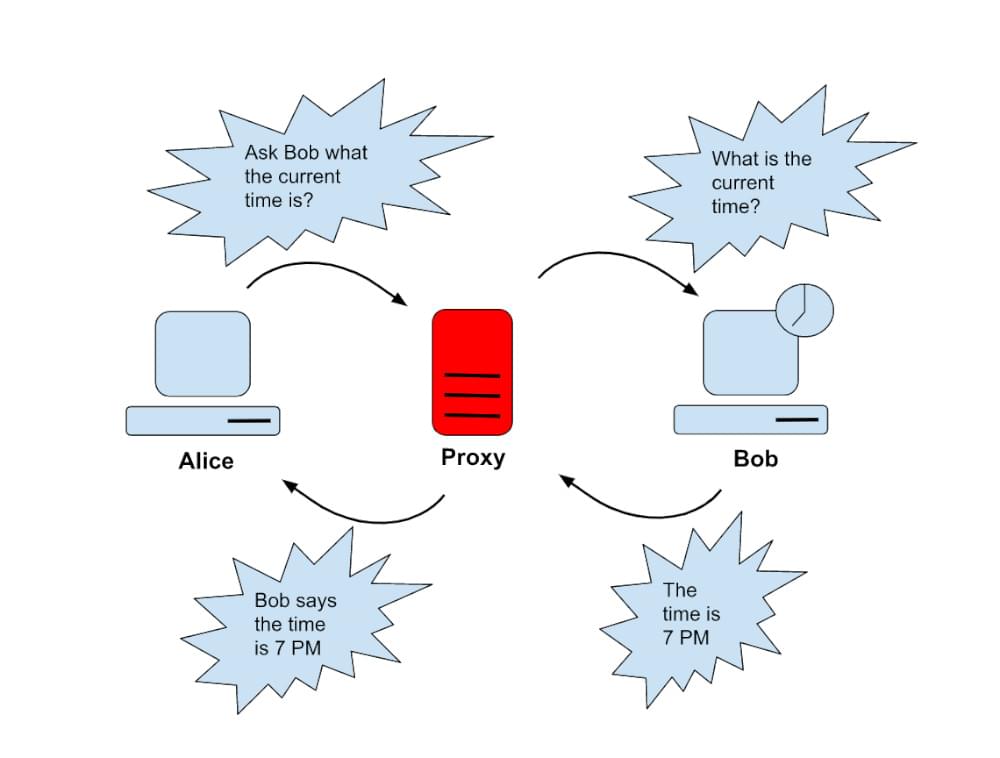
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your computer and the internet. Instead of connecting directly to a website or online service, your request is routed through the proxy server. The proxy then forwards your request to the destination server and relays the response back to you. This intermediary role offers several advantages, including anonymity, security, and access control.
Types of Proxy Servers
Several types of proxy servers cater to specific needs and use cases. Understanding these different types is crucial for selecting the right proxy for your requirements.
HTTP Proxies
HTTP proxies are designed specifically for handling web traffic. They are commonly used for caching web pages, filtering content, and providing anonymity when browsing the internet. When you access a website through an HTTP proxy, the proxy server retrieves the web page on your behalf and sends it back to you. This can improve browsing speed, reduce bandwidth consumption, and enhance privacy.
SOCKS Proxies
SOCKS proxies are more versatile than HTTP proxies and can handle any type of network traffic, including email, FTP, and peer-to-peer file sharing. SOCKS proxies operate at a lower level of the network stack, providing a more generic and flexible solution for routing traffic. They are often used to bypass firewalls and access blocked content. SOCKS5 is the latest version and offers improved security and performance compared to older versions.
Transparent Proxies
Transparent proxies, also known as intercepting proxies, are deployed without the user’s knowledge or configuration. They are commonly used by organizations to monitor and control internet usage. Transparent proxies can filter content, block access to certain websites, and cache web pages to improve network performance. While they offer benefits for network administrators, they can also raise privacy concerns for users.
Anonymous Proxies
Anonymous proxies conceal your IP address from the destination server, providing a degree of anonymity when browsing the internet. However, some anonymous proxies may still reveal that you are using a proxy server. Elite anonymous proxies, on the other hand, provide the highest level of anonymity by completely hiding your IP address and the fact that you are using a proxy.
Residential Proxies
Residential proxies use IP addresses assigned to real residential addresses, making them appear as legitimate users to websites and online services. This makes them more difficult to detect and block compared to datacenter proxies, which use IP addresses assigned to data centers. Residential proxies are often used for web scraping, ad verification, and social media management.
Datacenter Proxies
Datacenter proxies use IP addresses assigned to data centers. They are typically faster and more reliable than residential proxies but are also more easily detected and blocked. Datacenter proxies are often used for tasks that require high bandwidth and low latency, such as streaming video or downloading large files.
Proxy Examples in Action
Let’s explore some specific proxy examples to illustrate their practical applications.
Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
Many websites and online services restrict access based on geographical location. For example, a streaming service may only be available in certain countries. By using a proxy server located in an allowed region, you can bypass these geo-restrictions and access content that would otherwise be unavailable. This is a common use case for VPNs, which often incorporate proxy technology.
Enhancing Online Security
Proxies can enhance your online security by masking your IP address and encrypting your traffic. This makes it more difficult for hackers and cybercriminals to track your online activity and steal your personal information. Additionally, some proxy servers include built-in security features such as malware scanning and intrusion detection.
Improving Website Performance
Proxies can improve website performance by caching frequently accessed content. When a user requests a web page, the proxy server can serve the cached version instead of retrieving it from the origin server. This reduces latency and improves response times, resulting in a faster and more responsive user experience. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) often utilize proxy servers to distribute content across multiple locations, further enhancing performance.
Web Scraping
Web scraping involves extracting data from websites. However, many websites block or limit access from automated scraping tools. By using a proxy server, you can rotate your IP address and avoid being blocked. Residential proxies are particularly useful for web scraping as they are less likely to be detected than datacenter proxies. This allows businesses to gather valuable data for market research, competitive analysis, and other purposes.
Ad Verification
Advertisers use proxies to verify that their ads are being displayed correctly and reaching the intended audience. By using proxies located in different geographical regions, advertisers can simulate user access from various locations and ensure that their ads are being displayed as intended. This helps prevent ad fraud and ensures that advertising campaigns are effective.
Social Media Management
Social media managers often use proxies to manage multiple social media accounts. By using a different proxy for each account, they can avoid being flagged for suspicious activity. This allows them to automate tasks such as posting updates, following users, and liking content without violating the social media platform’s terms of service. Residential proxies are particularly useful for social media management as they are less likely to be detected than datacenter proxies.
Choosing the Right Proxy
Selecting the right proxy server depends on your specific needs and requirements. Consider the following factors when choosing a proxy:
- Anonymity Level: Do you need complete anonymity, or is a basic level of privacy sufficient?
- Speed and Reliability: How important is speed and reliability for your application?
- Location: Do you need a proxy server located in a specific geographical region?
- Cost: How much are you willing to spend on a proxy service?
- Security: What security features does the proxy server offer?
Potential Drawbacks of Using Proxies
While proxies offer numerous benefits, it’s essential to acknowledge potential drawbacks. Some free proxy services may log your activity or inject advertisements into web pages. Additionally, some proxies may be slow or unreliable, impacting your browsing experience. It’s crucial to choose a reputable proxy provider and understand the potential risks involved.
Conclusion
Understanding proxy examples and their diverse applications is essential in today’s digital world. From enhancing online security to bypassing geographical restrictions, proxies offer a versatile solution for individuals and organizations alike. By carefully considering your needs and selecting the right proxy server, you can leverage the benefits of this powerful technology. Remember to prioritize security and choose reputable providers to mitigate potential risks. The use of proxy servers continues to evolve, adapting to the ever-changing landscape of internet security and access. As technology advances, so too will the capabilities and applications of proxy servers, making them an increasingly important tool for navigating the online world. Whether you are looking to protect your privacy, access blocked content, or improve website performance, understanding the different types of proxy servers and their use cases is a valuable asset. This comprehensive overview of proxy examples should provide a solid foundation for making informed decisions about incorporating proxies into your online strategy. The increasing reliance on internet connectivity for both personal and professional activities underscores the importance of understanding and utilizing tools like proxy servers to enhance security, privacy, and access. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest advancements in proxy technology will be crucial for maintaining a secure and efficient online presence. Therefore, a thorough understanding of proxy examples is not just beneficial, but increasingly necessary in the modern digital age.
[See also: What is a Proxy Server?]
[See also: Types of Proxy Servers]
[See also: How to Use a Proxy Server]
[See also: Proxy vs VPN]
