Ubuntu Show IP: Comprehensive Guide to Finding Your IP Address
Understanding how to find your IP address on an Ubuntu system is crucial for various networking tasks, troubleshooting, and system administration. Whether you’re setting up a server, configuring network settings, or simply need to know your IP for remote access, this comprehensive guide will walk you through multiple methods to ubuntu show ip. We will cover command-line tools, graphical interfaces, and even external services to ensure you have all the necessary knowledge at your fingertips. Mastering the art of finding your IP address on Ubuntu is a fundamental skill for any Linux user. This article provides a clear, concise, and fact-checked explanation of several methods to ubuntu show ip.
Why is Knowing Your IP Address Important?
Before diving into the methods, let’s understand why knowing your IP address is important. An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. It serves two main functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing. Knowing your IP address allows you to:
- Configure network settings and troubleshoot connectivity issues.
- Access your computer remotely.
- Set up port forwarding for specific applications.
- Identify your network location.
- Diagnose network-related problems.
Methods to Ubuntu Show IP Address
There are several methods to ubuntu show ip. We’ll explore the most common and reliable ones, starting with command-line tools, then moving to graphical methods, and finally, using external services.
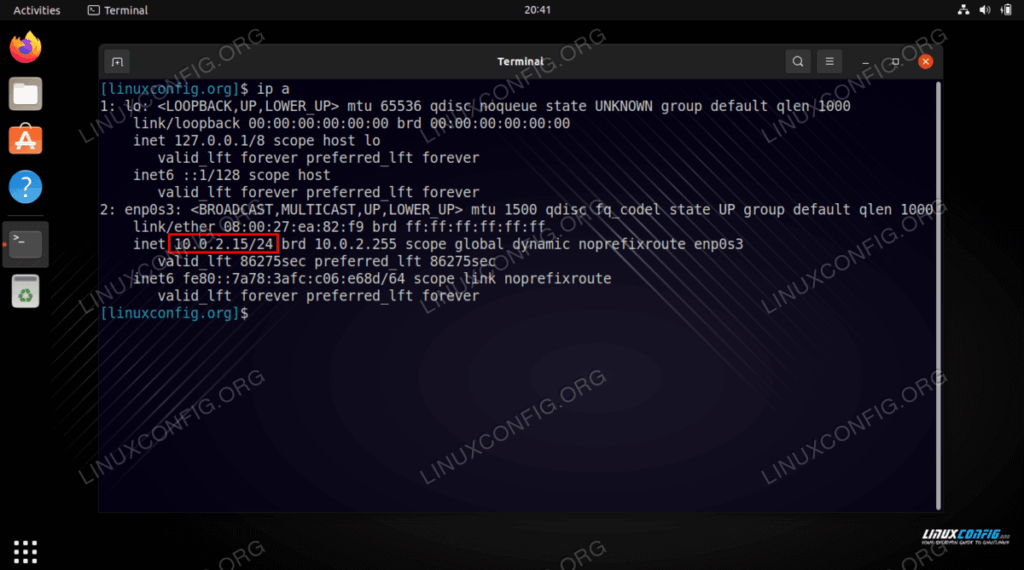
Using the `ip addr` Command
The `ip addr` command is a powerful command-line tool used for displaying and manipulating network interfaces. It’s part of the `iproute2` suite and is a modern replacement for older tools like `ifconfig`. Here’s how to use it to ubuntu show ip:
- Open a terminal window.
- Type `ip addr` and press Enter.
- Look for the network interface you are interested in (e.g., `eth0`, `wlan0`).
- Under the interface, find the line that starts with `inet`. The IP address is listed there.
For example:
ip addr
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:11:22:33:44:55 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.100/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::211:22ff:fe33:4455/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
In this example, the IP address for `eth0` is `192.168.1.100`.
Using the `hostname -I` Command
The `hostname -I` command provides a quick and easy way to display the IP addresses assigned to the host. It’s a simple command that directly outputs the IP addresses. To ubuntu show ip using this method:
- Open a terminal window.
- Type `hostname -I` and press Enter.
- The command will output the IP addresses, separated by spaces if there are multiple.
For example:
hostname -I
192.168.1.100
This method is particularly useful for scripting or when you need a quick way to retrieve the IP address without parsing the output of more complex commands.
Using the `ifconfig` Command (Deprecated but Still Common)
The `ifconfig` command was the traditional tool for configuring and displaying network interfaces. While it’s deprecated in favor of `ip`, it’s still widely used and available on many systems. To ubuntu show ip using `ifconfig`:
- Open a terminal window.
- Type `ifconfig` and press Enter.
- Look for the network interface you are interested in (e.g., `eth0`, `wlan0`).
- Under the interface, find the line that starts with `inet addr`. The IP address is listed there.
For example:
ifconfig
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:11:22:33:44:55
inet addr:192.168.1.100 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::211:22ff:fe33:4455/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:12345 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:67890 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:12345678 (12.3 MB) TX bytes:87654321 (87.6 MB)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
RX packets:123 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:123 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:12345 (12.3 KB) TX bytes:12345 (12.3 KB)
In this example, the IP address for `eth0` is `192.168.1.100`. If `ifconfig` is not found you may need to install it using `sudo apt install net-tools`.
Using `nmcli` (NetworkManager Command Line Interface)
`nmcli` is a command-line tool for controlling NetworkManager, which manages network connections on Ubuntu. It’s a versatile tool that can provide detailed information about network connections, including IP addresses. To ubuntu show ip using `nmcli`:
- Open a terminal window.
- Type `nmcli device show <interface>` (replace <interface> with your network interface, e.g., `eth0` or `wlan0`) and press Enter.
- Look for the `IP4.ADDRESS` field in the output. This field contains the IP address.
For example:
nmcli device show eth0
GENERAL.DEVICE: eth0
GENERAL.TYPE: ethernet
GENERAL.HWADDR: 00:11:22:33:44:55
GENERAL.MTU: 1500
GENERAL.STATE: 100 (connected)
GENERAL.CONNECTION: Wired connection 1
GENERAL.CON-PATH: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/1
IP4.ADDRESS[1]: 192.168.1.100/24
IP4.GATEWAY: 192.168.1.1
IP4.DNS[1]: 8.8.8.8
IP4.DNS[2]: 8.8.4.4
IP6.ADDRESS[1]: fe80::211:22ff:fe33:4455/64
IP6.GATEWAY: --
IP6.DNS[1]: --
In this example, the IP address for `eth0` is `192.168.1.100`.
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Method
If you prefer using a graphical interface, Ubuntu provides a straightforward way to find your IP address through the system settings. This method is particularly useful for users who are not comfortable with the command line. To ubuntu show ip using the GUI:
- Click on the system menu in the top-right corner of the screen.
- Select “Settings”.
- In the Settings window, click on “Network”.
- Select the network connection you are using (e.g., Ethernet or Wi-Fi).
- The IP address is displayed under the “Details” section.
The network settings window provides a clear and user-friendly way to view your IP address, along with other network information such as the gateway and DNS servers.
Using External Services (WhatIsMyIP)
Sometimes, you need to know your public IP address, which is the IP address assigned to your network by your internet service provider (ISP). This is different from your private IP address, which is used within your local network. You can use external services to ubuntu show ip public address:
- Open a web browser.
- Go to a website like WhatIsMyIP.com, IPLocation.net or IPChicken.com.
- The website will display your public IP address.
These websites use JavaScript to detect your IP address and display it on the page. They are a convenient way to quickly find your public IP address without having to use command-line tools or navigate through system settings.
Using `curl` to Find External IP
If you prefer using the command line and need to find your external IP address, you can use the `curl` command along with a service that returns your IP. Here’s how to ubuntu show ip using `curl`:
- Open a terminal window.
- Type `curl ifconfig.me` or `curl ipinfo.io/ip` or `curl api.ipify.org` and press Enter.
- The command will output your public IP address.
For example:
curl ifconfig.me
203.0.113.45
These services provide a simple API that returns your IP address in plain text, making it easy to use with command-line tools like `curl`.
Troubleshooting IP Address Issues
Sometimes, you may encounter issues with your IP address, such as not being able to obtain an IP address or having an incorrect IP address. Here are some common troubleshooting steps:
- Restart your network interface: Use the command `sudo ifdown eth0 && sudo ifup eth0` (replace `eth0` with your network interface).
- Renew your DHCP lease: Use the command `sudo dhclient eth0` (replace `eth0` with your network interface).
- Check your network configuration: Ensure that your network settings are configured correctly, including the gateway and DNS servers.
- Restart your router: Sometimes, simply restarting your router can resolve IP address issues.
If you continue to experience issues, consult your network administrator or ISP for further assistance. Understanding how to ubuntu show ip is just the first step; knowing how to troubleshoot related issues is equally important.
Conclusion
Knowing how to ubuntu show ip address is a fundamental skill for anyone using Ubuntu. Whether you prefer using command-line tools like `ip addr`, `hostname -I`, `ifconfig`, or `nmcli`, or prefer a graphical interface, there are multiple methods available to suit your needs. Additionally, using external services like WhatIsMyIP or `curl` can help you find your public IP address. By mastering these techniques, you’ll be well-equipped to configure network settings, troubleshoot connectivity issues, and manage your Ubuntu system effectively. Remember to choose the method that best suits your comfort level and the specific task at hand. This comprehensive guide provides all the information you need to confidently ubuntu show ip and manage your network settings. [See also: Understanding Network Interfaces in Linux] and [See also: Troubleshooting Network Connectivity Issues in Ubuntu].
