Understanding the Medicare Conversion Factor: What It Means for Healthcare Providers and Patients
The Medicare conversion factor is a critical component of the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS), influencing how healthcare providers are reimbursed for services rendered to Medicare beneficiaries. This factor, updated annually, directly impacts the financial stability of medical practices and the accessibility of healthcare services for millions of Americans. Understanding the intricacies of the Medicare conversion factor is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients to navigate the complex landscape of healthcare financing.
What is the Medicare Conversion Factor?
The Medicare conversion factor is a dollar amount that translates relative value units (RVUs) into actual payment amounts for physician services under Medicare Part B. RVUs are assigned to each medical service based on the resources required to provide it, including physician work, practice expense, and malpractice insurance. The Medicare conversion factor essentially sets the price per RVU, determining the base payment rate before adjustments for geographic location or other factors.
Think of it like this: each medical procedure has a price tag in RVUs. The Medicare conversion factor is the exchange rate that converts those RVUs into dollars. A higher Medicare conversion factor means higher payments for each service, while a lower factor results in lower payments.
How is the Medicare Conversion Factor Calculated?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) calculates the Medicare conversion factor annually. The process involves several steps, including:
- Estimating Medicare spending: CMS projects total Medicare spending for physician services in the coming year.
- Applying budget neutrality adjustments: These adjustments ensure that changes to the fee schedule do not significantly increase or decrease overall Medicare spending.
- Accounting for legislative changes: Congress may pass laws that affect the Medicare conversion factor, such as temporary payment increases or sequestration cuts.
The resulting Medicare conversion factor is then published in the annual MPFS final rule. This rule outlines all the changes to Medicare payment policies for the upcoming year.
The Impact of Changes to the Medicare Conversion Factor
Changes to the Medicare conversion factor can have significant consequences for healthcare providers and patients. A decrease in the Medicare conversion factor can lead to:
- Reduced physician payments: Lower payments can strain medical practices, especially those that rely heavily on Medicare revenue.
- Potential service cuts: Some providers may choose to reduce or eliminate certain services if they are no longer financially viable.
- Decreased access to care: Patients may face longer wait times or have difficulty finding physicians who accept Medicare.
Conversely, an increase in the Medicare conversion factor can:
- Improve physician financial stability: Higher payments can help medical practices invest in new technology, hire staff, and expand services.
- Maintain or improve access to care: Providers are more likely to continue offering services and accepting Medicare patients.
The Medicare conversion factor is a crucial element in the financial health of the healthcare system. Small changes can have ripple effects throughout the industry, impacting both providers and patients.
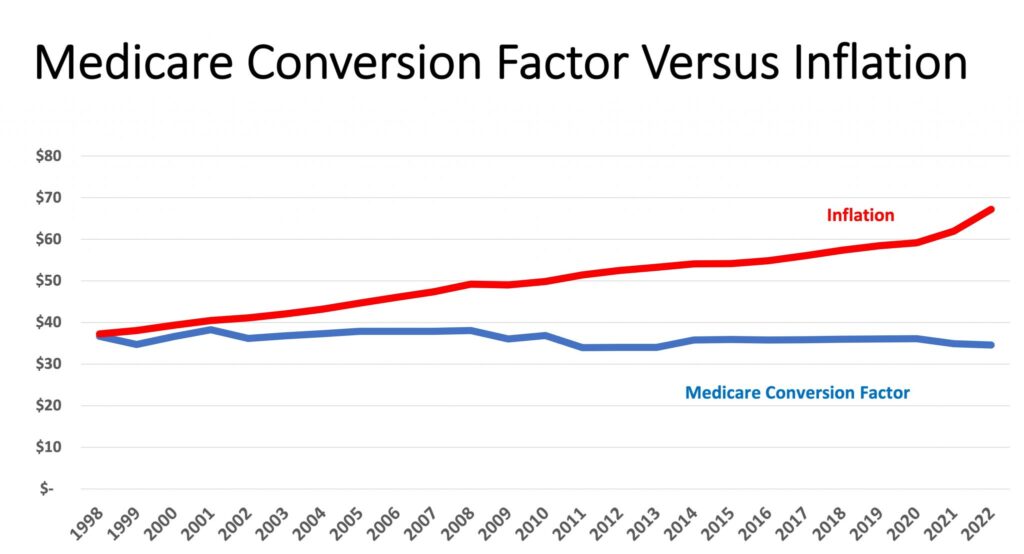
Recent History and Current Status of the Medicare Conversion Factor
In recent years, the Medicare conversion factor has been subject to significant volatility. Budget sequestration and other legislative actions have resulted in temporary payment cuts, creating uncertainty for healthcare providers. For example, the 2023 Medicare conversion factor saw a significant decrease, raising concerns about access to care. This decrease prompted lobbying efforts from medical organizations to urge Congress to intervene and mitigate the impact.
The American Medical Association (AMA) and other physician groups have consistently advocated for a more stable and predictable Medicare conversion factor. They argue that the current system creates unnecessary administrative burden and makes it difficult for practices to plan for the future. [See also: AMA Advocacy for Medicare Reform]
The Role of Advocacy and Legislative Action
Advocacy plays a crucial role in shaping the Medicare conversion factor. Medical organizations, patient advocacy groups, and individual healthcare providers all have a voice in the process. By communicating their concerns to lawmakers and CMS, they can influence policy decisions and help ensure that the Medicare conversion factor adequately reflects the cost of providing high-quality care.
Legislative action is often necessary to address long-term challenges related to the Medicare conversion factor. Congress has the power to enact permanent reforms to the MPFS and ensure that physicians are fairly compensated for their services. [See also: Medicare Payment Reform Legislation]
The Future of the Medicare Conversion Factor
The future of the Medicare conversion factor is uncertain. As healthcare costs continue to rise, policymakers face difficult decisions about how to balance the need to control spending with the need to ensure access to care. Several potential reforms are being discussed, including:
- Value-based payment models: These models reward providers for delivering high-quality, cost-effective care, rather than simply paying for volume.
- Alternative payment models (APMs): APMs encourage collaboration and coordination among healthcare providers.
- Updates to the RVU system: Some stakeholders argue that the current RVU system does not accurately reflect the cost of providing certain services.
Ultimately, the future of the Medicare conversion factor will depend on the willingness of policymakers to address the underlying challenges facing the healthcare system. A sustainable solution will require a collaborative effort from all stakeholders, including providers, patients, payers, and policymakers.
Understanding the Medicare Conversion Factor for Patients
While the Medicare conversion factor may seem like a technical detail, it directly impacts patients. A stable and adequate Medicare conversion factor helps ensure that physicians continue to accept Medicare, allowing beneficiaries access to the care they need. When the Medicare conversion factor is cut, physicians may limit the number of Medicare patients they see, impacting access, particularly for those in rural areas or with chronic conditions.
Patients can stay informed about the Medicare conversion factor and its implications by:
- Following news and updates from patient advocacy groups: These groups often provide information about legislative efforts and policy changes that affect Medicare.
- Contacting their elected officials: Patients can share their concerns about access to care and urge lawmakers to support policies that protect Medicare beneficiaries.
- Staying informed about changes to their Medicare coverage: CMS provides information about changes to Medicare benefits and payment policies on its website.
The Medicare Conversion Factor and its Effect on Rural Healthcare
The Medicare conversion factor has a disproportionate impact on rural healthcare. Rural areas often face challenges in attracting and retaining physicians due to lower reimbursement rates and higher overhead costs. When the Medicare conversion factor is reduced, rural practices may struggle to stay afloat, leading to closures and reduced access to care for rural communities. [See also: Challenges in Rural Healthcare Access]
Telehealth and other innovative technologies can help mitigate some of the challenges facing rural healthcare, but these solutions require adequate funding and support. Policymakers need to consider the unique needs of rural communities when making decisions about the Medicare conversion factor and other Medicare payment policies.
Conclusion
The Medicare conversion factor is a critical component of the Medicare payment system, impacting healthcare providers, patients, and the overall accessibility of care. Understanding its complexities and advocating for a sustainable and predictable system is essential for ensuring that Medicare beneficiaries have access to the high-quality care they deserve. Staying informed, engaging in advocacy efforts, and supporting legislative solutions are all crucial steps in protecting the future of Medicare and the health of our nation.
The annual adjustments to the Medicare conversion factor require constant vigilance. Healthcare providers must adapt to these changes to maintain their financial viability, while patients need to understand how these adjustments can affect their access to medical services. The Medicare conversion factor is more than just a number; it is a key determinant of the health and well-being of millions of Americans.
