Unveiling the Power of Web Crawler Applications: A Comprehensive Guide
In the vast digital landscape, where information is constantly being generated and updated, the ability to efficiently extract and organize data from the web is paramount. This is where web crawler applications, also known as spiders or bots, come into play. These sophisticated tools automatically browse the World Wide Web, systematically following links and gathering information according to predefined rules. This article delves into the world of web crawler applications, exploring their functionalities, applications, and the underlying principles that govern their operation.
What is a Web Crawler Application?
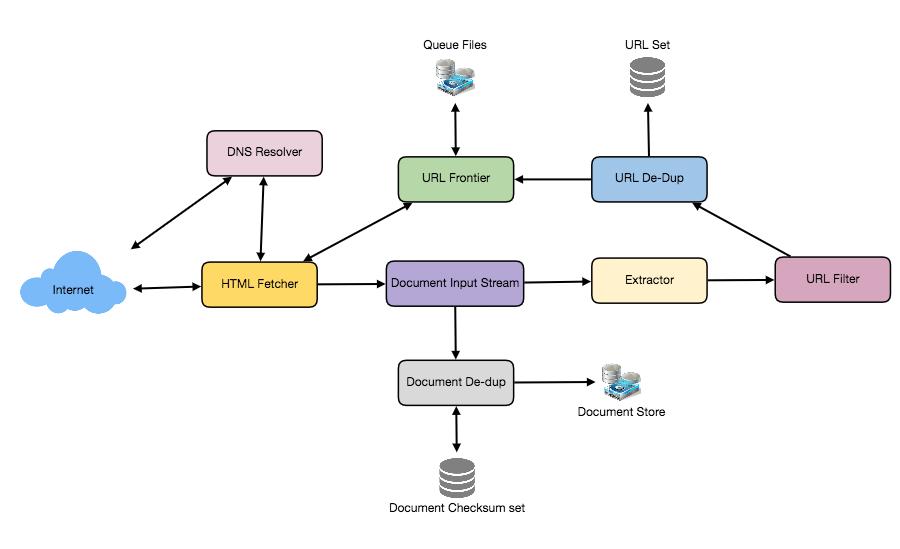
A web crawler application is essentially an automated program designed to traverse the internet in a methodical and structured manner. Unlike human users who manually browse web pages, a web crawler application can rapidly navigate through thousands, even millions, of websites, extracting specific data points or indexing the entire content of each page. The process typically begins with a list of URLs, known as a “seed set,” which serves as the starting point for the crawler. The web crawler application then visits these URLs, extracts the content, and identifies all the hyperlinks present on the page. These hyperlinks are added to a queue, and the crawler continues to visit and extract data from these newly discovered URLs, repeating the process until a predefined stopping condition is met.
How Web Crawlers Work
The operation of a web crawler application can be broken down into several key stages:
- Initialization: The crawler starts with a seed set of URLs.
- Fetching: The crawler sends HTTP requests to the URLs in the queue to retrieve the corresponding web pages.
- Parsing: The fetched HTML content is parsed to extract relevant information, such as text, images, and hyperlinks.
- Extraction: Specific data points are extracted based on predefined rules or patterns.
- Indexing: The extracted data is indexed and stored in a database for efficient retrieval.
- Following Links: The crawler identifies and extracts all hyperlinks from the fetched page.
- Queueing: The extracted hyperlinks are added to the queue for future crawling.
- Policy Enforcement: The crawler adheres to various policies, such as robots.txt, to avoid overloading servers or accessing restricted content.
Applications of Web Crawler Applications
Web crawler applications have a wide range of applications across various industries and domains:
Search Engine Indexing
Perhaps the most well-known application is search engine indexing. Search engines like Google, Bing, and DuckDuckGo rely heavily on web crawler applications to discover and index the vast amount of content available on the internet. These crawlers systematically explore the web, identifying new pages and updating their indexes to ensure that search results are accurate and relevant.
Data Mining and Research
Researchers and data analysts use web crawler applications to gather data for various research projects. For example, a researcher studying social media trends might use a crawler to collect data from Twitter or Facebook. Similarly, a market analyst might use a crawler to gather pricing information from e-commerce websites.
Price Comparison
Price comparison websites utilize web crawler applications to gather product prices from different online retailers. This allows consumers to easily compare prices and find the best deals.
Monitoring and Alerting
Web crawler applications can be used to monitor websites for changes or updates. For example, a company might use a crawler to monitor its competitors’ websites for new product releases or price changes. They can also be used to monitor news websites for mentions of a particular company or brand.
SEO Auditing
SEO professionals use web crawler applications to analyze websites and identify areas for improvement. These crawlers can identify broken links, missing meta descriptions, and other issues that can negatively impact a website’s search engine ranking. [See also: SEO Audit Checklist]
Archiving
Organizations like the Internet Archive use web crawler applications to create archives of the web. These archives allow users to access past versions of websites, providing a valuable resource for researchers and historians.
Ethical Considerations and Best Practices
While web crawler applications are powerful tools, it’s important to use them ethically and responsibly. Uncontrolled crawling can overload servers, consume excessive bandwidth, and potentially violate website terms of service. Here are some best practices to consider:
- Respect robots.txt: The robots.txt file is a standard text file that specifies which parts of a website should not be crawled. It’s crucial to respect these directives to avoid accessing restricted content.
- Limit request rate: Avoid making too many requests to a website in a short period of time. This can overload the server and potentially lead to your crawler being blocked. Implement delays between requests to be respectful of the server’s resources.
- Identify your crawler: Include a User-Agent header in your HTTP requests that clearly identifies your crawler. This allows website administrators to easily identify and contact you if necessary.
- Handle errors gracefully: Implement error handling to gracefully handle situations where a website is unavailable or returns an error code.
- Avoid crawling sensitive data: Be mindful of the data you are collecting and avoid crawling sensitive or private information.
- Comply with terms of service: Always review and comply with the terms of service of the websites you are crawling.
Building Your Own Web Crawler Application
Several programming languages and libraries can be used to build web crawler applications. Python, with its rich ecosystem of libraries like Beautiful Soup and Scrapy, is a popular choice. Here’s a simplified example of how to build a basic web crawler using Python and Beautiful Soup:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
def crawl(url):
try:
response = requests.get(url)
response.raise_for_status() # Raise HTTPError for bad responses (4xx or 5xx)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.content, 'html.parser')
# Extract data (e.g., title, links)
title = soup.title.text
print(f"Title: {title}")
for link in soup.find_all('a'):
href = link.get('href')
if href:
print(f"Link: {href}")
# Optionally, recursively crawl the link
# crawl(href) # Be cautious about recursion!
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"Error crawling {url}: {e}")
# Example usage
seed_url = 'https://www.example.com'
crawl(seed_url)
This example demonstrates the basic steps involved in fetching a web page, parsing its HTML content, and extracting the title and links. A more robust web crawler application would require additional features such as queue management, politeness policies, and data storage.
The Future of Web Crawling
As the web continues to evolve, web crawler applications are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning are enabling crawlers to better understand the content they are extracting and to adapt to the ever-changing structure of the web. We can expect to see future crawlers that are more intelligent, efficient, and ethical in their operation. The ability to handle dynamic content rendered by JavaScript, navigate complex website structures, and extract structured data with greater accuracy will be key to the future of web crawler applications. [See also: The Impact of AI on Web Crawling]
Conclusion
Web crawler applications are indispensable tools for navigating and extracting information from the vast expanse of the World Wide Web. From powering search engines to enabling data mining and research, these applications play a crucial role in our digital world. By understanding the principles behind their operation and adhering to ethical best practices, we can harness the power of web crawler applications to unlock valuable insights and drive innovation. The continued development of more sophisticated and intelligent web crawler applications will undoubtedly shape the future of information access and analysis on the internet. A well-designed web crawler application is a powerful asset for any organization that needs to gather and analyze data from the web, and is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in today’s information-driven economy. Using a web crawler application effectively requires careful planning and execution, but the rewards are well worth the effort.
