Using Proxy Servers: A Comprehensive Guide for Enhanced Security and Privacy
In today’s interconnected world, online security and privacy are paramount. One effective method for safeguarding your digital footprint is by using proxy servers. A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your computer and the internet, masking your IP address and providing an extra layer of security. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of using proxy servers, covering everything from their functionality to their various applications and limitations.
What is a Proxy Server?
A proxy server is essentially a gateway between you and the internet. When you use a proxy, your internet traffic flows through the proxy server on its way to the destination address. The destination server then perceives the traffic as originating from the proxy server, not your computer. This process effectively conceals your IP address, which is a unique identifier for your device on the internet.
How Proxy Servers Work
The process of using a proxy involves several key steps:
- Request: Your computer sends a request to access a specific website or online resource.
- Redirection: The request is routed to the proxy server.
- Masking: The proxy server masks your IP address with its own.
- Forwarding: The proxy server forwards the request to the destination server.
- Response: The destination server sends the response back to the proxy server.
- Delivery: The proxy server forwards the response to your computer.
This entire process happens seamlessly in the background, allowing you to browse the internet without directly exposing your IP address. By using proxy servers, you are effectively creating a buffer between your device and the outside world.
Types of Proxy Servers
There are several types of proxy servers, each offering different features and levels of security:
HTTP Proxies
HTTP proxies are designed for web traffic. They handle HTTP requests, which are used for accessing websites. These proxies are relatively simple to set up and are commonly used with proxy services for basic web browsing anonymity. However, they typically don’t encrypt traffic, making them less secure than other options.
HTTPS Proxies (SSL Proxies)
HTTPS proxies, also known as SSL proxies, encrypt the traffic between your computer and the proxy server. This encryption adds an extra layer of security, protecting your data from eavesdropping. Using proxy servers with HTTPS support is crucial when dealing with sensitive information, such as online banking or e-commerce transactions.
SOCKS Proxies
SOCKS proxies are more versatile than HTTP proxies. They can handle any type of traffic, including web browsing, email, and file transfers. SOCKS proxies also support various authentication methods, making them more secure. Using proxy servers with SOCKS protocols offers greater flexibility and security for various online activities. SOCKS5 is the most commonly used version, offering improved speed and security over older versions.
Transparent Proxies
Transparent proxies, also known as intercepting proxies, do not hide your IP address. Instead, they are typically used by organizations to monitor and filter internet traffic. These proxies are often found in schools, libraries, and workplaces. While they don’t provide anonymity, they can still be beneficial for content filtering and security purposes. You might be using a proxy like this without even realizing it.
Anonymous Proxies
Anonymous proxies hide your IP address but identify themselves as proxies. This type of proxy provides a moderate level of anonymity. While your IP address is concealed, websites can still detect that you are using a proxy. This is often sufficient for casual browsing and accessing geo-restricted content.
Elite Proxies (Highly Anonymous Proxies)
Elite proxies, also known as highly anonymous proxies, hide both your IP address and the fact that you are using a proxy. This type of proxy provides the highest level of anonymity. Websites cannot detect that you are using a proxy, making it appear as if you are browsing directly from your own computer. This is ideal for users who require maximum privacy and security.
Benefits of Using Proxy Servers
Using proxy servers offers numerous advantages:
- Enhanced Privacy: Proxies mask your IP address, making it difficult for websites and third parties to track your online activities.
- Improved Security: Proxies can provide an extra layer of security by filtering malicious content and preventing direct access to your computer.
- Access to Geo-Restricted Content: Proxies allow you to bypass geographical restrictions and access content that is not available in your region.
- Bypassing Censorship: Proxies can be used to circumvent censorship and access blocked websites and online services.
- Load Balancing: Proxies can distribute network traffic across multiple servers, improving performance and preventing overload.
- Caching: Proxies can cache frequently accessed content, reducing bandwidth usage and improving website loading times.
Potential Drawbacks of Using Proxy Servers
While using proxy servers offers many benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider:
- Slower Connection Speed: Routing traffic through a proxy server can sometimes slow down your internet connection.
- Security Risks: Some proxy servers may be insecure and could potentially expose your data to malicious actors.
- Logging: Some proxy servers log user activity, which could compromise your privacy.
- Compatibility Issues: Some websites and online services may not work properly with certain proxy servers.
- Cost: While many free proxy servers are available, they often come with limitations and security risks. Premium proxy services typically offer better performance and security but come at a cost.
How to Choose the Right Proxy Server
Selecting the right proxy server depends on your specific needs and requirements. Consider the following factors:
- Security: Choose a proxy server that offers robust security features, such as encryption and authentication.
- Speed: Look for a proxy server with fast connection speeds to minimize performance impact.
- Reliability: Select a proxy server with a high uptime and reliable performance.
- Location: Choose a proxy server located in a region that allows you to access the content you need.
- Cost: Consider your budget and choose a proxy server that offers the best value for your money.
- Logging Policy: Review the proxy server’s logging policy to ensure that your privacy is protected.
Setting Up a Proxy Server
Setting up a proxy server is relatively straightforward. The process varies depending on your operating system and web browser. Here are the general steps:
Windows
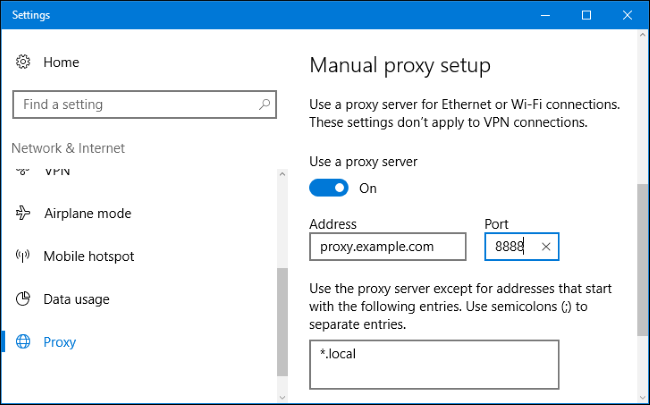
- Open the Control Panel.
- Click on Internet Options.
- Go to the Connections tab.
- Click on LAN Settings.
- Check the box next to “Use a proxy server for your LAN.”
- Enter the proxy server address and port number.
- Click OK to save the settings.
macOS
- Open System Preferences.
- Click on Network.
- Select your network connection (e.g., Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
- Click on Advanced.
- Go to the Proxies tab.
- Select the type of proxy server you want to use (e.g., HTTP or SOCKS).
- Enter the proxy server address and port number.
- Click OK to save the settings.
Web Browsers
Most web browsers also allow you to configure proxy settings directly. The steps vary depending on the browser:
- Chrome: Go to Settings > Advanced > System > Open your computer’s proxy settings.
- Firefox: Go to Options > General > Network Settings > Settings.
- Safari: Follow the macOS instructions above.
Common Use Cases for Proxy Servers
Using proxy servers is common in several scenarios:
- Bypassing Geo-Restrictions: Accessing streaming services or websites that are not available in your region.
- Protecting Privacy on Public Wi-Fi: Masking your IP address when using public Wi-Fi networks.
- Web Scraping: Automating data collection from websites without being blocked.
- Social Media Management: Managing multiple social media accounts without being flagged.
- Online Gaming: Improving connection stability and reducing lag in online games.
- Research: Conducting research anonymously without revealing your identity.
Free vs. Paid Proxy Servers
Both free and paid proxy servers are available. Free proxy servers are often slower, less reliable, and may come with security risks. Paid proxy servers typically offer better performance, security, and customer support. If you require a high level of security and reliability, a paid proxy server is generally the better option. Using proxy services that are paid often provide a more stable experience.
The Future of Proxy Servers
As internet security and privacy concerns continue to grow, the demand for proxy servers is likely to increase. New technologies and protocols are constantly being developed to improve the performance and security of proxy servers. In the future, we can expect to see more sophisticated proxy solutions that offer even greater levels of anonymity and protection. The importance of using proxy servers for privacy and security will only continue to grow.
Conclusion
Using proxy servers is an effective way to enhance your online security and privacy. By masking your IP address and routing your traffic through an intermediary server, you can protect your data from prying eyes and access content that is otherwise restricted. While there are some potential drawbacks to consider, the benefits of using proxy servers often outweigh the risks. By understanding the different types of proxy servers and how they work, you can choose the right solution for your specific needs and enjoy a safer and more private online experience. Whether you are using a proxy for personal or professional reasons, it is a valuable tool for navigating the digital world.
[See also: VPN vs Proxy: Which is Better for Your Online Security?]
[See also: How to Set Up a Proxy Server on Windows 10]
[See also: The Best Proxy Server Providers for 2024]
