What are HTTP Cookies: A Comprehensive Guide
In the ever-evolving landscape of the internet, understanding the mechanisms that facilitate seamless online experiences is crucial. One such mechanism, often operating behind the scenes, is the HTTP cookie. This guide delves into the world of what are HTTP cookies, exploring their purpose, functionality, types, and implications for user privacy and security.
Understanding the Basics of HTTP Cookies
What are HTTP cookies? Simply put, they are small text files that websites store on a user’s computer. These files contain data that the website can retrieve later. Think of them as digital breadcrumbs that allow websites to remember information about you, such as your login details, preferences, or items in your shopping cart.
HTTP cookies are essential for creating personalized and efficient web experiences. Without them, websites would treat every request as a brand new one, making tasks like staying logged in or maintaining a shopping cart virtually impossible.
How HTTP Cookies Work
The process of using HTTP cookies is relatively straightforward:
- A user visits a website.
- The website sends an HTTP response to the user’s browser, including a Set-Cookie header.
- The browser stores the cookie on the user’s computer.
- When the user revisits the same website, the browser sends the cookie back to the server in the HTTP request header.
- The server can then use the information stored in the cookie to identify the user and provide a tailored experience.
This cycle allows websites to maintain state across multiple requests, making the internet a more user-friendly place.
Types of HTTP Cookies
What are HTTP cookies classified into? There are several types of HTTP cookies, each serving a different purpose:
- Session Cookies: These cookies are temporary and are deleted when the user closes their browser. They are primarily used to maintain session state, such as keeping a user logged in during a single browsing session.
- Persistent Cookies: These cookies remain on the user’s computer for a specified period, even after the browser is closed. They are used to remember user preferences, login details, and other information for future visits.
- First-Party Cookies: These cookies are set by the website that the user is currently visiting. They are typically used to enhance the user experience on that specific website.
- Third-Party Cookies: These cookies are set by a domain different from the website the user is visiting. They are often used for tracking user behavior across multiple websites and are commonly associated with advertising networks.
- Secure Cookies: These cookies are only transmitted over HTTPS connections, providing an extra layer of security. They prevent the cookie from being intercepted by attackers on insecure networks.
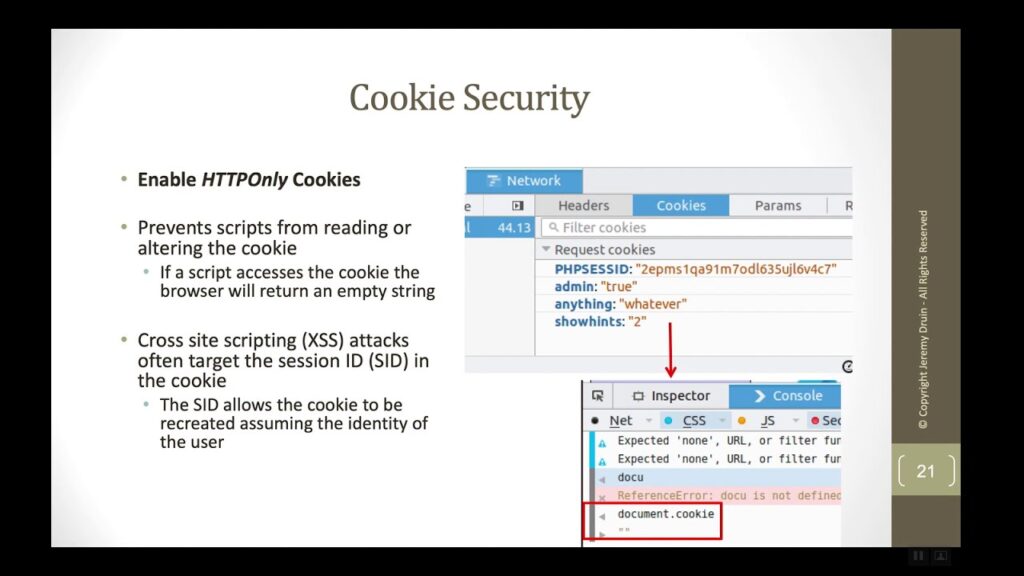
- HTTPOnly Cookies: These cookies cannot be accessed by client-side scripts, such as JavaScript. This helps to prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
Understanding the different types of HTTP cookies is crucial for both website developers and users concerned about privacy and security.
The Role of HTTP Cookies in Web Development
What are HTTP cookies used for in web development? They play a vital role in numerous web applications, including:
- Session Management: Maintaining user sessions and keeping users logged in.
- Personalization: Remembering user preferences, such as language settings or theme choices.
- Tracking: Monitoring user behavior and collecting data for analytics purposes.
- E-commerce: Storing items in a shopping cart and facilitating the checkout process.
- Authentication: Verifying user identities and granting access to restricted areas of a website.
Without HTTP cookies, many of the features we take for granted on the web would not be possible. They provide a simple yet powerful mechanism for storing and retrieving user-specific information.
Privacy and Security Concerns
While HTTP cookies offer numerous benefits, they also raise privacy and security concerns. Third-party cookies, in particular, have been criticized for their role in tracking user behavior across the web. This data can be used to create detailed profiles of users, which can then be used for targeted advertising or other purposes. [See also: Data Privacy Regulations]
Furthermore, HTTP cookies can be vulnerable to security attacks, such as cross-site scripting (XSS) and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). Attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to steal cookies and gain unauthorized access to user accounts.
To mitigate these risks, it is important to implement proper security measures, such as using secure cookies and HTTPOnly cookies. Users can also take steps to protect their privacy by clearing their cookies regularly and using privacy-focused browsers or browser extensions.
Managing HTTP Cookies
Most web browsers provide tools for managing HTTP cookies. Users can view, delete, and block cookies, as well as configure their browser to accept or reject cookies from specific websites. [See also: Browser Security Settings]
To manage cookies in Chrome, for example, you can go to Settings > Privacy and security > Cookies and other site data. From there, you can view and delete cookies, block third-party cookies, and configure other cookie settings.
Other browsers offer similar options for managing HTTP cookies. By taking control of their cookie settings, users can better protect their privacy and security online.
The Future of HTTP Cookies
The landscape of HTTP cookies is constantly evolving. As privacy concerns continue to grow, there is increasing pressure on websites and advertising networks to find alternative ways to track user behavior. [See also: Privacy-Enhancing Technologies]
One promising alternative is the use of privacy-preserving technologies, such as differential privacy and federated learning. These technologies allow websites to collect and analyze user data without compromising individual privacy.
Another trend is the shift towards first-party data. Websites are increasingly focusing on collecting data directly from their users, rather than relying on third-party cookies. This allows them to build more direct relationships with their customers and provide more personalized experiences.
What are HTTP cookies going to look like in the future? While their role may evolve, it is likely that they will continue to play an important part in the functioning of the web for the foreseeable future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, what are HTTP cookies? They are small text files that websites use to store information on a user’s computer. They play a crucial role in enabling personalized and efficient web experiences, but they also raise privacy and security concerns. By understanding how HTTP cookies work and how to manage them, users can better protect their privacy and security online. As the web continues to evolve, it is important to stay informed about the latest developments in cookie technology and privacy-preserving alternatives.
The understanding of what are HTTP cookies is paramount for anyone navigating the digital world, from casual users to seasoned developers. Embracing this knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their online privacy and security.
The ongoing debate surrounding what are HTTP cookies and their implications highlights the need for a balanced approach, one that respects user privacy while still enabling the functionality and personalization that users have come to expect from the web.
Furthermore, staying updated on the latest advancements and regulations regarding what are HTTP cookies is essential for businesses and developers alike. Compliance with privacy laws and ethical data handling practices is crucial for maintaining trust and ensuring a sustainable digital ecosystem.
Finally, the discussion on what are HTTP cookies serves as a reminder of the importance of digital literacy and critical thinking in the modern age. By educating ourselves and others about the technologies that shape our online experiences, we can foster a more informed and responsible approach to the internet.
