What is a Proxy on WiFi? Understanding Proxy Servers and WiFi Networks
In today’s interconnected world, understanding the nuances of network configurations is crucial for both personal and professional internet usage. One such configuration involves using a proxy server on a WiFi network. But what is a proxy on WiFi, and why might you want to use one? This article aims to demystify proxy servers in the context of WiFi networks, exploring their functionality, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Understanding Proxy Servers
Before delving into the specifics of using a proxy with WiFi, it’s essential to understand what a proxy server is in general. A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. Instead of your device directly connecting to a website or online service, your request is first routed through the proxy server. The proxy then forwards the request on your behalf and relays the response back to you.
Think of it like a translator. You speak English, but the person you need to communicate with only understands Spanish. The translator (proxy server) listens to your English, translates it to Spanish, relays it to the other person, translates their Spanish response back to English, and relays it to you. This process masks your direct communication and provides a layer of abstraction.
Types of Proxy Servers
Proxy servers come in various forms, each offering different levels of security and functionality:
- HTTP Proxies: Primarily used for web traffic, handling HTTP requests and responses.
- HTTPS Proxies: Similar to HTTP proxies but encrypt the data transmitted between your device and the proxy server, providing enhanced security.
- SOCKS Proxies: More versatile than HTTP proxies, capable of handling various types of traffic, including email, FTP, and torrents. They operate at a lower level and offer greater flexibility.
- Transparent Proxies: These proxies don’t modify requests but are often used for caching or filtering content. Users might not even be aware they are using a transparent proxy.
- Anonymous Proxies: Designed to hide your IP address and other identifying information, making it more difficult to track your online activity.
- Reverse Proxies: Used by servers to distribute incoming requests to multiple backend servers, improving performance and security. This is typically used on the server-side, not the client-side.
WiFi Networks and Their Vulnerabilities
WiFi networks have become ubiquitous, providing convenient internet access in homes, offices, and public spaces. However, they are not without their vulnerabilities. Public WiFi networks, in particular, can be risky due to the lack of encryption and security measures. Hackers can intercept data transmitted over these networks, potentially compromising sensitive information like passwords, credit card details, and personal data.
Even private WiFi networks can be susceptible to attacks if they are not properly secured. Weak passwords, outdated firmware, and misconfigured settings can create vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit.
Using a Proxy on WiFi: Why and How
Now that we understand proxy servers and WiFi network vulnerabilities, let’s explore why you might want to use a proxy on WiFi. Using a proxy server on a WiFi network offers several potential benefits:
Enhanced Security
One of the primary reasons to use a proxy on WiFi is to enhance your online security. By routing your traffic through a proxy server, you can mask your IP address, making it more difficult for websites and attackers to track your location and identify your device. Additionally, some proxy servers offer encryption, protecting your data from being intercepted by eavesdroppers on public WiFi networks.
Accessing Geo-Restricted Content
Another common use case for proxies on WiFi is accessing geo-restricted content. Many websites and streaming services restrict access based on the user’s location. By using a proxy server located in a different region, you can bypass these restrictions and access content that would otherwise be unavailable. For example, if you’re traveling abroad and want to watch a TV show that’s only available in your home country, you can use a proxy server located in your home country to access the show.
Bypassing Censorship
In some countries, governments censor internet content, blocking access to certain websites and online services. A proxy on WiFi can be used to bypass these censorship measures, allowing users to access information freely. By routing traffic through a proxy server located in a country with less restrictive internet policies, users can circumvent censorship and access blocked content.
Improved Performance
In some cases, using a proxy on WiFi can improve your internet performance. Some proxy servers cache frequently accessed content, reducing the need to repeatedly download the same data. This can result in faster loading times and a more responsive browsing experience. However, it’s important to note that not all proxy servers offer caching, and some may even slow down your connection due to increased latency.
Content Filtering and Monitoring
Organizations often use proxy servers on their WiFi networks to filter content and monitor employee internet usage. This can help to prevent employees from accessing inappropriate websites, reduce the risk of malware infections, and ensure compliance with company policies. Content filtering can also be used to block access to social media sites or other distractions during work hours.
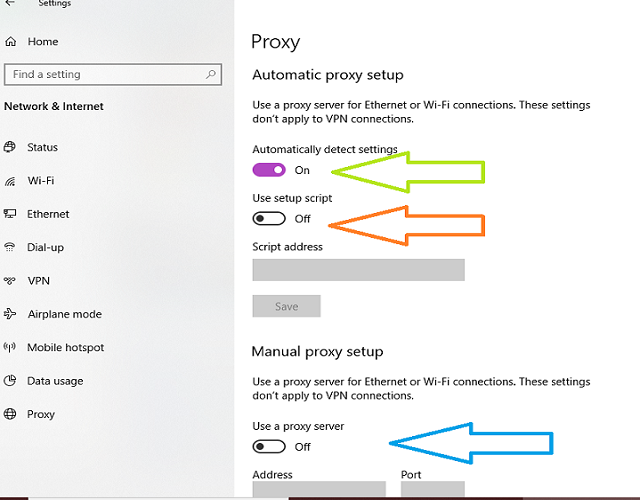
Configuring a Proxy on WiFi
Configuring a proxy on WiFi typically involves modifying your device’s network settings. The exact steps may vary depending on your operating system and device type, but the general process is similar:
- Obtain Proxy Server Details: You’ll need the IP address and port number of the proxy server you want to use. This information is usually provided by your proxy server provider or network administrator.
- Access Network Settings: On your device, go to the network settings and select the WiFi network you’re connected to.
- Configure Proxy Settings: Look for the proxy settings section and enable the use of a proxy server. Enter the IP address and port number of the proxy server.
- Save Changes: Save the changes to your network settings and restart your browser or other applications to ensure the proxy settings are applied.
Many modern operating systems and browsers also support automatic proxy configuration using a Proxy Auto-Configuration (PAC) file. A PAC file is a script that specifies how web browsers and other user agents should automatically choose an appropriate proxy server for fetching a given URL. This simplifies the proxy configuration process and allows network administrators to easily manage proxy settings for multiple users.
Potential Drawbacks of Using a Proxy on WiFi
While using a proxy on WiFi offers several benefits, it’s also important to be aware of the potential drawbacks:
Slower Connection Speed
As mentioned earlier, some proxy servers can slow down your internet connection due to increased latency. This is especially true for free or public proxy servers, which are often overloaded with users. Choosing a reputable and reliable proxy server provider can help to minimize this issue.
Security Risks
Not all proxy servers are created equal. Some proxy servers may be operated by malicious actors who are looking to steal your data or infect your device with malware. It’s crucial to choose a proxy server provider that you trust and to avoid using free or public proxy servers unless you are certain of their security.
Logging and Monitoring
Proxy servers can log your internet activity, including the websites you visit and the data you transmit. This information can be used for various purposes, such as monitoring employee internet usage or tracking user behavior for marketing purposes. If you’re concerned about privacy, choose a proxy server provider that has a clear and transparent privacy policy and that does not log your activity.
Compatibility Issues
Some websites and applications may not be compatible with proxy servers. This can result in errors or unexpected behavior. If you encounter compatibility issues, you may need to disable the proxy server for that specific website or application.
Choosing the Right Proxy Server
When choosing a proxy server for use on your WiFi network, consider the following factors:
- Security: Look for a proxy server provider that offers encryption and other security measures to protect your data.
- Reliability: Choose a proxy server provider that has a reputation for reliability and uptime.
- Speed: Test the speed of the proxy server to ensure it doesn’t significantly slow down your internet connection.
- Location: Choose a proxy server located in a region that meets your needs, whether it’s for accessing geo-restricted content or bypassing censorship.
- Privacy: Read the proxy server provider’s privacy policy to understand how they handle your data.
- Cost: Compare the prices of different proxy server providers and choose one that fits your budget.
There are numerous providers offering proxy services. Researching and comparing options is important. Look for reviews and testimonials from other users to get a sense of the provider’s reliability and performance. [See also: Best Proxy Server Providers of 2024]
Alternatives to Proxy Servers
While proxy servers can be useful in certain situations, there are also alternatives that may be more suitable for some users:
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs encrypt all of your internet traffic and route it through a secure server, providing a higher level of security and privacy than proxy servers. [See also: What is a VPN and How Does it Work?]
- Tor Browser: Tor is a free and open-source browser that anonymizes your internet traffic by routing it through a network of relays. This makes it very difficult to track your online activity. [See also: Anonymity Online: The Power of Tor Browser]
- HTTPS Everywhere: HTTPS Everywhere is a browser extension that automatically encrypts your connection to websites that support HTTPS. This helps to protect your data from being intercepted by eavesdroppers.
Conclusion
Understanding what is a proxy on WiFi and how it works is vital in today’s digital landscape. Using a proxy server on a WiFi network can offer several benefits, including enhanced security, access to geo-restricted content, and bypassing censorship. However, it’s also important to be aware of the potential drawbacks, such as slower connection speed and security risks. By carefully considering your needs and choosing a reputable proxy server provider, you can leverage the benefits of proxy servers while minimizing the risks. Always prioritize security and privacy when browsing the internet, especially on public WiFi networks. Whether you are looking to improve performance, bypass geo-restrictions, or simply enhance your online security, a proxy on WiFi can be a valuable tool. Remember to weigh the pros and cons and choose a solution that best fits your individual needs and risk tolerance.
