What is SSL Inspection: A Comprehensive Guide to Secure Network Monitoring
In today’s digital landscape, securing network traffic is paramount. As more and more internet traffic becomes encrypted using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and its successor, Transport Layer Security (TLS), organizations face the challenge of maintaining visibility into that traffic for security purposes. This is where SSL inspection comes into play. But what is SSL inspection exactly, and why is it so crucial for modern network security? This article will delve into the intricacies of SSL inspection, exploring its benefits, challenges, and best practices.
Understanding SSL/TLS Encryption
Before diving into SSL inspection, it’s essential to understand the underlying technology it addresses: SSL/TLS encryption. SSL/TLS protocols are designed to provide secure communication over a network. They achieve this by encrypting data transmitted between a client (e.g., a web browser) and a server (e.g., a website). This encryption ensures that eavesdroppers cannot intercept and read the data being exchanged.
However, this very encryption poses a problem for network security. While it protects sensitive data from malicious actors, it also hides malicious content from security devices. Malware, phishing attacks, and data exfiltration attempts can all be concealed within encrypted traffic, making them difficult to detect and prevent.
The Need for SSL Inspection
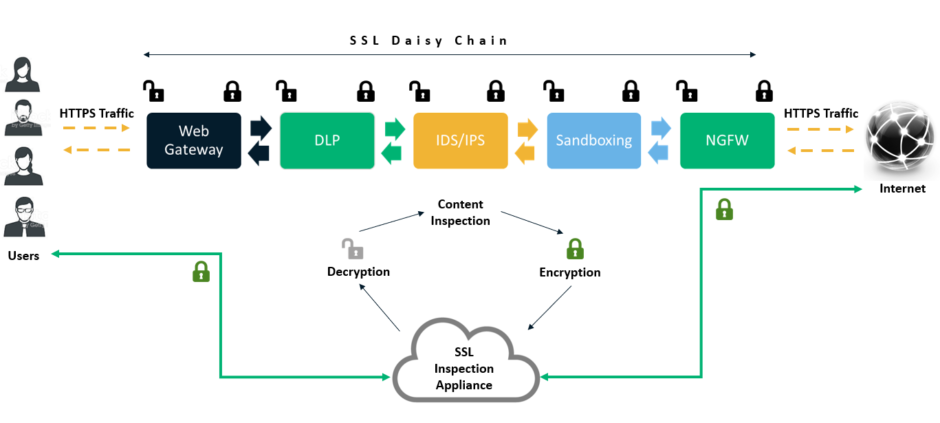
The increasing prevalence of SSL/TLS encryption has created a blind spot for traditional security tools. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and other security appliances are unable to inspect the contents of encrypted traffic without SSL inspection. This lack of visibility can leave networks vulnerable to a wide range of threats.
SSL inspection, also known as SSL decryption or SSL interception, addresses this problem by intercepting and decrypting SSL/TLS traffic. This allows security devices to inspect the traffic for malicious content, policy violations, and other security risks. Once the traffic has been inspected, it is re-encrypted and forwarded to its destination.
How SSL Inspection Works
The process of SSL inspection typically involves the following steps:
- Interception: The SSL inspection device intercepts the SSL/TLS connection between the client and the server.
- Decryption: The device decrypts the encrypted traffic using the server’s private key (or a certificate installed on the device itself).
- Inspection: The decrypted traffic is inspected by security devices for malicious content, policy violations, and other security risks.
- Re-encryption: After inspection, the traffic is re-encrypted using a new SSL/TLS certificate.
- Forwarding: The re-encrypted traffic is forwarded to its original destination.
There are two primary modes of SSL inspection:
- SSL Forward Proxy: In this mode, the SSL inspection device acts as a proxy for outbound traffic. Clients are configured to send all their traffic to the proxy, which then performs SSL inspection before forwarding the traffic to the server.
- SSL Reverse Proxy: In this mode, the SSL inspection device acts as a proxy for inbound traffic. The device intercepts all incoming SSL/TLS connections to a server and performs SSL inspection before forwarding the traffic to the server.
Benefits of SSL Inspection
Implementing SSL inspection offers several significant benefits for network security:
- Enhanced Threat Detection: SSL inspection allows security devices to inspect encrypted traffic for malware, phishing attacks, and other threats that would otherwise be hidden.
- Improved Data Loss Prevention (DLP): By inspecting encrypted traffic, organizations can prevent sensitive data from being exfiltrated from their network.
- Compliance: SSL inspection can help organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements by ensuring that all network traffic is properly inspected for security risks.
- Application Control: SSL inspection enables organizations to enforce policies on the use of specific applications and services, even when those applications are using encryption.
Challenges of SSL Inspection
While SSL inspection offers numerous benefits, it also presents several challenges:
- Performance Impact: Decrypting and re-encrypting SSL/TLS traffic can be resource-intensive and can impact network performance.
- Privacy Concerns: SSL inspection involves intercepting and decrypting user traffic, which raises privacy concerns. Organizations must implement appropriate policies and safeguards to protect user privacy.
- Certificate Management: SSL inspection requires managing SSL/TLS certificates, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Compatibility Issues: Some applications and services may not be compatible with SSL inspection, which can lead to connectivity problems.
Best Practices for SSL Inspection
To mitigate the challenges of SSL inspection and maximize its benefits, organizations should follow these best practices:
- Implement a comprehensive privacy policy: Clearly communicate to users how their traffic is being inspected and what data is being collected.
- Use a dedicated SSL inspection appliance: Avoid using general-purpose security devices for SSL inspection, as they may not have the performance capacity to handle the workload.
- Implement selective SSL inspection: Only inspect traffic that is deemed to be high-risk, such as traffic to known malicious websites or traffic containing sensitive data.
- Exclude sensitive categories: Exclude categories like health, finance, and other sensitive categories from SSL inspection to avoid violating user privacy.
- Regularly update certificates: Keep SSL/TLS certificates up-to-date to prevent security vulnerabilities.
- Monitor performance: Continuously monitor network performance to ensure that SSL inspection is not negatively impacting user experience.
- Provide user education: Educate users about the benefits of SSL inspection and the steps being taken to protect their privacy.
SSL Inspection and Privacy
One of the most significant concerns surrounding SSL inspection is its potential impact on user privacy. Because SSL inspection involves decrypting user traffic, it raises questions about data security and the potential for misuse of sensitive information.
To address these concerns, organizations must implement robust privacy policies and safeguards. These policies should clearly define how user traffic is being inspected, what data is being collected, and how that data is being protected. Organizations should also implement technical controls to minimize the amount of data that is collected and to prevent unauthorized access to that data. [See also: Data Loss Prevention Strategies].
Furthermore, organizations should be transparent with users about their SSL inspection practices. Users should be informed that their traffic is being inspected and should be given the opportunity to opt out of SSL inspection if they choose. This transparency can help to build trust and alleviate privacy concerns.
The Future of SSL Inspection
As encryption becomes even more prevalent, SSL inspection will become increasingly important for network security. However, the challenges of SSL inspection are also likely to grow. Organizations will need to find new and innovative ways to inspect encrypted traffic without impacting performance or compromising user privacy. [See also: Next-Generation Firewall Features]
One potential solution is the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence to identify malicious content within encrypted traffic without the need for full decryption. These technologies can analyze traffic patterns and identify anomalies that may indicate a security threat. This approach can help to reduce the performance impact of SSL inspection and minimize privacy concerns.
Another trend is the increasing use of TLS 1.3, the latest version of the TLS protocol. TLS 1.3 offers several security enhancements, but it also makes SSL inspection more difficult. Organizations will need to adapt their SSL inspection practices to accommodate TLS 1.3.
Conclusion
SSL inspection is a critical component of modern network security. By intercepting and decrypting SSL/TLS traffic, organizations can gain visibility into encrypted traffic and protect their networks from a wide range of threats. However, SSL inspection also presents several challenges, including performance impact, privacy concerns, and certificate management. By following best practices and implementing appropriate policies and safeguards, organizations can mitigate these challenges and maximize the benefits of SSL inspection. As encryption continues to evolve, SSL inspection will remain an essential tool for securing networks and protecting sensitive data. Understanding what is SSL inspection, its implications, and how to implement it effectively is crucial for any organization striving to maintain a robust security posture. [See also: Network Security Best Practices]
