What is SSL Inspection: A Comprehensive Guide to Security and Privacy
In today’s digital landscape, securing online communications is paramount. One critical technology used to achieve this is Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), now more commonly known as Transport Layer Security (TLS). However, the very encryption that protects data can also be exploited by malicious actors to conceal threats. This is where SSL inspection comes into play. This article delves into what SSL inspection is, how it works, its benefits, potential drawbacks, and best practices for implementation.
Understanding SSL/TLS Encryption
Before diving into what SSL inspection entails, it’s essential to grasp the basics of SSL/TLS encryption. SSL/TLS creates a secure tunnel between a client (e.g., a web browser) and a server. This tunnel encrypts all data transmitted, preventing eavesdropping and tampering. When you see a padlock icon in your browser’s address bar, it signifies that an SSL/TLS connection is active.
The encryption process involves cryptographic keys. The server presents a digital certificate to the client, verifying its identity. The client and server then negotiate a shared secret key used to encrypt and decrypt data. This process ensures confidentiality and integrity.
The Need for SSL Inspection
While SSL/TLS safeguards data, it also presents a challenge for network security. Cybercriminals can hide malware, ransomware, and other malicious content within encrypted traffic, bypassing traditional security measures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems. This is where SSL inspection becomes crucial. By decrypting and inspecting SSL/TLS traffic, organizations can identify and block hidden threats.
Imagine a scenario where an employee unknowingly downloads a file containing malware over an encrypted connection. Without SSL inspection, the network security devices would be blind to the threat, allowing it to potentially compromise the entire network. With SSL inspection, the file would be decrypted, scanned for malware, and blocked if found to be malicious.
How SSL Inspection Works
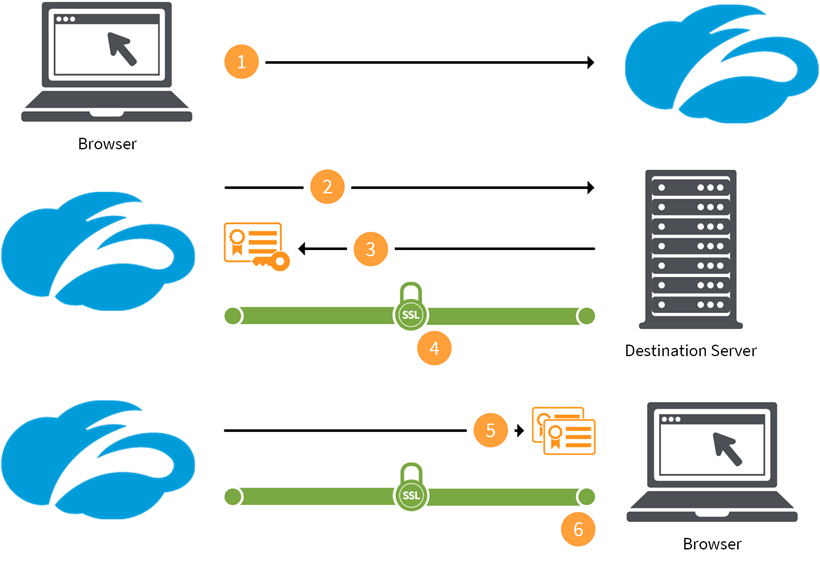
SSL inspection, also known as SSL decryption or TLS inspection, involves intercepting and decrypting SSL/TLS traffic, inspecting its content, and then re-encrypting it before forwarding it to its destination. This process typically occurs within a dedicated security appliance or software solution.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
- Interception: The SSL inspection device intercepts the SSL/TLS handshake between the client and the server.
- Decryption: The device decrypts the SSL/TLS traffic using the server’s certificate (or a generated certificate).
- Inspection: The decrypted traffic is inspected for malicious content, such as malware, viruses, or data leakage.
- Re-encryption: After inspection, the traffic is re-encrypted using a new SSL/TLS certificate issued by the SSL inspection device.
- Forwarding: The re-encrypted traffic is then forwarded to the intended destination.
This process allows security devices to analyze the content of encrypted traffic and enforce security policies effectively. It’s vital for maintaining a secure network environment.
Benefits of SSL Inspection
Implementing SSL inspection offers several significant benefits for organizations:
- Enhanced Threat Detection: It allows for the detection of malware, ransomware, and other malicious content hidden within encrypted traffic.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): It enables the inspection of encrypted traffic for sensitive data, preventing data leakage.
- Compliance: It helps organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements that mandate the monitoring and protection of sensitive data.
- Improved Visibility: It provides greater visibility into network traffic, allowing security teams to identify and respond to potential threats more effectively.
- Application Control: It allows for the control of encrypted application traffic, ensuring that only authorized applications are used on the network.
By decrypting and inspecting SSL/TLS traffic, organizations can significantly improve their security posture and reduce the risk of cyberattacks.
Potential Drawbacks of SSL Inspection
While SSL inspection offers numerous benefits, it also presents some potential drawbacks that organizations need to consider:
- Performance Impact: Decrypting and re-encrypting traffic can be resource-intensive, potentially impacting network performance.
- Privacy Concerns: Inspecting encrypted traffic raises privacy concerns, as it involves accessing and analyzing user data.
- Complexity: Implementing and managing SSL inspection can be complex, requiring specialized expertise and resources.
- Certificate Management: Managing SSL/TLS certificates for SSL inspection can be challenging, especially in large organizations.
- Compatibility Issues: Some applications and websites may not be compatible with SSL inspection, leading to connectivity issues.
It’s crucial to carefully weigh the benefits and drawbacks before implementing SSL inspection and to implement it in a way that minimizes potential negative impacts.
Best Practices for Implementing SSL Inspection
To ensure successful and effective SSL inspection implementation, consider the following best practices:
- Define Clear Policies: Establish clear policies regarding what traffic will be inspected and how the data will be handled.
- Obtain User Consent: Obtain user consent for SSL inspection, especially in environments where privacy is a concern.
- Choose the Right Solution: Select an SSL inspection solution that meets your organization’s specific needs and requirements. Consider factors such as performance, scalability, and ease of management.
- Optimize Performance: Optimize the performance of your SSL inspection solution to minimize the impact on network performance. This may involve using hardware acceleration or load balancing.
- Monitor and Analyze Traffic: Continuously monitor and analyze traffic to identify potential threats and ensure that SSL inspection is working effectively.
- Regularly Update Certificates: Regularly update SSL/TLS certificates to prevent certificate-related issues and ensure compatibility.
- Implement Exceptions: Create exceptions for applications and websites that are known to be incompatible with SSL inspection.
- Provide Training: Provide training to security teams on how to use and manage the SSL inspection solution.
By following these best practices, organizations can effectively implement SSL inspection while minimizing potential drawbacks and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
SSL Inspection and Privacy Considerations
SSL inspection inevitably raises privacy concerns, as it involves decrypting and analyzing user data. It’s crucial to address these concerns proactively by implementing appropriate safeguards.
Here are some key considerations:
- Transparency: Be transparent with users about SSL inspection and its purpose. Clearly communicate what data is being inspected and how it is being used.
- Data Minimization: Minimize the amount of data that is inspected. Only inspect traffic that is deemed necessary for security purposes.
- Data Security: Ensure that decrypted data is stored securely and protected from unauthorized access.
- Compliance with Regulations: Comply with all applicable privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Anonymization: Consider anonymizing data where possible to protect user privacy.
By addressing privacy concerns proactively, organizations can build trust with users and ensure that SSL inspection is implemented in a responsible and ethical manner.
The Future of SSL Inspection
As encryption technologies continue to evolve, SSL inspection will need to adapt to stay ahead of emerging threats. One trend to watch is the increasing use of TLS 1.3, which offers enhanced security and performance compared to previous versions. SSL inspection solutions will need to support TLS 1.3 to effectively inspect encrypted traffic.
Another trend is the growing adoption of cloud-based security solutions. Cloud-based SSL inspection offers several advantages, including scalability, flexibility, and ease of deployment. As more organizations migrate to the cloud, cloud-based SSL inspection will become increasingly important.
Finally, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is expected to play a growing role in SSL inspection. AI and ML can be used to analyze traffic patterns, detect anomalies, and identify potential threats more effectively than traditional security methods.
Conclusion
SSL inspection is a critical security technology that enables organizations to inspect encrypted traffic for threats. While it offers numerous benefits, it also presents potential drawbacks, such as performance impact and privacy concerns. By following best practices and addressing privacy concerns proactively, organizations can effectively implement SSL inspection and improve their security posture. As encryption technologies continue to evolve, SSL inspection will need to adapt to stay ahead of emerging threats. Understanding what SSL inspection is and how it works is essential for any organization looking to protect its network and data from cyberattacks. [See also: Network Security Best Practices] [See also: Understanding TLS 1.3] [See also: Data Loss Prevention Strategies]
